0001601712false2022Q1December 3100016017122022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:SeriesAPreferredStockMember2022-01-012022-03-3100016017122022-04-18xbrli:sharesiso4217:USD00016017122021-01-012021-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2021-01-012021-03-31iso4217:USDxbrli:shares00016017122022-03-3100016017122021-12-310001601712syf:UnsecuritizedLoansHeldforInvestmentMember2022-03-310001601712syf:UnsecuritizedLoansHeldforInvestmentMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:PreferredStockMember2020-12-310001601712us-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-12-310001601712us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2020-12-310001601712us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2020-12-310001601712us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2020-12-310001601712us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2020-12-3100016017122020-12-310001601712us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-01-012021-03-310001601712us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-01-012021-03-310001601712us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2021-01-012021-03-310001601712us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-01-012021-03-310001601712us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-01-012021-03-310001601712us-gaap:PreferredStockMember2021-03-310001601712us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-03-310001601712us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-03-310001601712us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-03-310001601712us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-03-310001601712us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2021-03-3100016017122021-03-310001601712us-gaap:PreferredStockMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:PreferredStockMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:USGovernmentCorporationsAndAgenciesSecuritiesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:USGovernmentCorporationsAndAgenciesSecuritiesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:USStatesAndPoliticalSubdivisionsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:USStatesAndPoliticalSubdivisionsMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:ResidentialMortgageBackedSecuritiesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:ResidentialMortgageBackedSecuritiesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:OtherDebtSecuritiesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:OtherDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-31xbrli:pure0001601712us-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:UnallocatedFinancingReceivablesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:UnallocatedFinancingReceivablesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:UnallocatedFinancingReceivablesMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2020-12-310001601712us-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2021-01-012021-03-310001601712us-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2021-03-310001601712us-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2020-12-310001601712us-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2021-01-012021-03-310001601712us-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2021-03-310001601712us-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2020-12-310001601712us-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2021-01-012021-03-310001601712us-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2021-03-310001601712us-gaap:UnallocatedFinancingReceivablesMember2020-12-310001601712us-gaap:UnallocatedFinancingReceivablesMember2021-01-012021-03-310001601712us-gaap:UnallocatedFinancingReceivablesMember2021-03-310001601712syf:FinancingReceivables30to89DaysPastDueMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FinancialAssetPastDueMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2022-03-310001601712syf:FinancingReceivables30to89DaysPastDueMemberus-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMemberus-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:ConsumerLoanMemberus-gaap:FinancialAssetPastDueMember2022-03-310001601712syf:FinancingReceivables30to89DaysPastDueMemberus-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMemberus-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMemberus-gaap:FinancialAssetPastDueMember2022-03-310001601712syf:FinancingReceivables30to89DaysPastDueMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FinancialAssetPastDueMember2022-03-310001601712syf:FinancingReceivables30to89DaysPastDueMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FinancialAssetPastDueMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2021-12-310001601712syf:FinancingReceivables30to89DaysPastDueMemberus-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMemberus-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:ConsumerLoanMemberus-gaap:FinancialAssetPastDueMember2021-12-310001601712syf:FinancingReceivables30to89DaysPastDueMemberus-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMemberus-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMemberus-gaap:FinancialAssetPastDueMember2021-12-310001601712syf:FinancingReceivables30to89DaysPastDueMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FinancialAssetPastDueMember2021-12-31syf:contract0001601712syf:SixHundredAndFiftyOneOrHigherMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2022-03-310001601712syf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOneToSixHundredAndFiftyMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2022-03-310001601712syf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOrLessMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2022-03-310001601712syf:SixHundredAndFiftyOneOrHigherMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2021-12-310001601712syf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOneToSixHundredAndFiftyMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2021-12-310001601712syf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOrLessMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2021-12-310001601712syf:SixHundredAndFiftyOneOrHigherMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2021-03-310001601712syf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOneToSixHundredAndFiftyMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2021-03-310001601712syf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOrLessMemberus-gaap:CreditCardReceivablesMember2021-03-310001601712syf:SixHundredAndFiftyOneOrHigherMemberus-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:ConsumerLoanMembersyf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOneToSixHundredAndFiftyMember2022-03-310001601712syf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOrLessMemberus-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2022-03-310001601712syf:SixHundredAndFiftyOneOrHigherMemberus-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:ConsumerLoanMembersyf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOneToSixHundredAndFiftyMember2021-12-310001601712syf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOrLessMemberus-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2021-12-310001601712syf:SixHundredAndFiftyOneOrHigherMemberus-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2021-03-310001601712us-gaap:ConsumerLoanMembersyf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOneToSixHundredAndFiftyMember2021-03-310001601712syf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOrLessMemberus-gaap:ConsumerLoanMember2021-03-310001601712syf:SixHundredAndFiftyOneOrHigherMemberus-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMembersyf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOneToSixHundredAndFiftyMember2022-03-310001601712syf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOrLessMemberus-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2022-03-310001601712syf:SixHundredAndFiftyOneOrHigherMemberus-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMembersyf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOneToSixHundredAndFiftyMember2021-12-310001601712syf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOrLessMemberus-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2021-12-310001601712syf:SixHundredAndFiftyOneOrHigherMemberus-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2021-03-310001601712us-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMembersyf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOneToSixHundredAndFiftyMember2021-03-310001601712syf:FiveHundredAndNinetyOrLessMemberus-gaap:CommercialPortfolioSegmentMember2021-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:OtherAssetsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:OtherAssetsMember2021-12-310001601712syf:InvestmentsFundingCommitmentMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CustomerRelatedIntangibleAssetsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CustomerRelatedIntangibleAssetsMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:ComputerSoftwareIntangibleAssetMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:ComputerSoftwareIntangibleAssetMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:CustomerRelatedIntangibleAssetsMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CustomerRelatedIntangibleAssetsMember2021-01-012021-03-310001601712us-gaap:CustomerContractsMemberus-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2021-01-012021-03-310001601712us-gaap:CustomerContractsMemberus-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:OtherExpenseMembersyf:FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsExcludingCustomerContractsMember2022-01-012022-03-310001601712us-gaap:OtherExpenseMembersyf:FiniteLivedIntangibleAssetsExcludingCustomerContractsMember2021-01-012021-03-310001601712syf:ProgramArrangerMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMembersrt:MinimumMembersyf:FixedSecuritizedBorrowingsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMembersrt:MaximumMembersyf:FixedSecuritizedBorrowingsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMembersyf:FixedSecuritizedBorrowingsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMembersyf:FixedSecuritizedBorrowingsMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMembersrt:MinimumMembersyf:FloatingSecuritizedBorrowingsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMembersrt:MaximumMembersyf:FloatingSecuritizedBorrowingsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMembersyf:FloatingSecuritizedBorrowingsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMembersyf:FloatingSecuritizedBorrowingsMember2021-12-310001601712srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembersyf:FixedSeniorUnsecuredNotesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembersrt:MaximumMembersyf:FixedSeniorUnsecuredNotesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembersyf:FixedSeniorUnsecuredNotesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembersyf:FixedSeniorUnsecuredNotesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembersrt:MaximumMembersrt:SubsidiariesMembersyf:FixedSeniorUnsecuredNotesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembersrt:SubsidiariesMembersyf:FixedSeniorUnsecuredNotesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembersrt:SubsidiariesMembersyf:FixedSeniorUnsecuredNotesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:UnsecuredDebtMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:USGovernmentCorporationsAndAgenciesSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:USGovernmentCorporationsAndAgenciesSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:USGovernmentCorporationsAndAgenciesSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:USGovernmentCorporationsAndAgenciesSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:USStatesAndPoliticalSubdivisionsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:USStatesAndPoliticalSubdivisionsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:USStatesAndPoliticalSubdivisionsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:USStatesAndPoliticalSubdivisionsMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:ResidentialMortgageBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:ResidentialMortgageBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:ResidentialMortgageBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:ResidentialMortgageBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:OtherDebtSecuritiesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:OtherDebtSecuritiesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:OtherDebtSecuritiesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:OtherDebtSecuritiesMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:USGovernmentCorporationsAndAgenciesSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:USGovernmentCorporationsAndAgenciesSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:USGovernmentCorporationsAndAgenciesSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:USGovernmentCorporationsAndAgenciesSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:USStatesAndPoliticalSubdivisionsMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:USStatesAndPoliticalSubdivisionsMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:USStatesAndPoliticalSubdivisionsMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:USStatesAndPoliticalSubdivisionsMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:ResidentialMortgageBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:ResidentialMortgageBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:ResidentialMortgageBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:ResidentialMortgageBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:AssetBackedSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:OtherDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:OtherDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:OtherDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:OtherDebtSecuritiesMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-03-310001601712us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310001601712us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001601712syf:BaselIIIMember2022-03-310001601712syf:BaselIIIMember2021-12-310001601712srt:SubsidiariesMembersyf:BaselIIIMember2022-03-310001601712srt:SubsidiariesMembersyf:BaselIIIMember2021-12-310001601712srt:MaximumMember2022-03-31
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-Q
| | | | | |
| ☒ | QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the quarterly period ended March 31, 2022
OR
| | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
001-36560
(Commission File Number)
SYNCHRONY FINANCIAL
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | | | | | | | |
| Delaware | | 51-0483352 |
(State or other jurisdiction of
incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer
Identification No.) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 777 Long Ridge Road | | |
| Stamford, | Connecticut | | 06902 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | | (Zip Code) |
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code) - (203) 585-2400
Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Common stock, par value $0.001 per share | SYF | New York Stock Exchange |
| Depositary Shares Each Representing a 1/40th Interest in a Share of 5.625% Fixed Rate Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock, Series A | SYFPrA | New York Stock Exchange |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large Accelerated Filer | ☒ | Accelerated Filer | ☐ |
| | | |
| Non-Accelerated Filer | ☐ | Smaller Reporting Company | ☐ |
| | | |
| | Emerging Growth Company | ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The number of shares of the registrant’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share, outstanding as of April 18, 2022 was 501,488,808.
Synchrony Financial
| | | | | |
| PART I - FINANCIAL INFORMATION | Page |
| |
| |
| Item 1. Financial Statements: | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| PART II - OTHER INFORMATION | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Item 6. Exhibits | |
| |
Certain Defined Terms
Except as the context may otherwise require in this report, references to:
•“we,” “us,” “our” and the “Company” are to SYNCHRONY FINANCIAL and its subsidiaries;
•“Synchrony” are to SYNCHRONY FINANCIAL only;
•the “Bank” are to Synchrony Bank (a subsidiary of Synchrony);
•the “Board of Directors” or “Board” are to Synchrony's board of directors;
•“CECL” are to the impairment model known as the Current Expected Credit Loss model, which is based on expected credit losses; and
•“VantageScore” are to a credit score developed by the three major credit reporting agencies which is used as a means of evaluating the likelihood that credit users will pay their obligations.
We provide a range of credit products through programs we have established with a diverse group of national and regional retailers, local merchants, manufacturers, buying groups, industry associations and healthcare service providers, which, in our business and in this report, we refer to as our “partners.” The terms of the programs all require cooperative efforts between us and our partners of varying natures and degrees to establish and operate the programs. Our use of the term “partners” to refer to these entities is not intended to, and does not, describe our legal relationship with them, imply that a legal partnership or other relationship exists between the parties or create any legal partnership or other relationship.
Unless otherwise indicated, references to “loan receivables” do not include loan receivables held for sale.
For a description of certain other terms we use, including “active account” and “purchase volume,” see the notes to “Management’s Discussion and Analysis—Results of Operations—Other Financial and Statistical Data” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021 (our “2021 Form 10-K”). There is no standard industry definition for many of these terms, and other companies may define them differently than we do.
“Synchrony” and its logos and other trademarks referred to in this report, including CareCredit®, Quickscreen®, Dual Card™, Synchrony Car Care™ and SyPI™, belong to us. Solely for convenience, we refer to our trademarks in this report without the ™ and ® symbols, but such references are not intended to indicate that we will not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, our rights to our trademarks. Other service marks, trademarks and trade names referred to in this report are the property of their respective owners.
On our website at www.synchronyfinancial.com, we make available under the "Investors-SEC Filings" menu selection, free of charge, our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and amendments to these reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after such reports or amendments are electronically filed with, or furnished to, the SEC. The SEC maintains an Internet site at www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information that we file electronically with the SEC.
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements:
Various statements in this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q may contain “forward-looking statements” as defined in Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), which are subject to the “safe harbor” created by those sections. Forward-looking statements may be identified by words such as “expects,” “intends,” “anticipates,” “plans,” “believes,” “seeks,” “targets,” “outlook,” “estimates,” “will,” “should,” “may” or words of similar meaning, but these words are not the exclusive means of identifying forward-looking statements.
Forward-looking statements are based on management’s current expectations and assumptions, and are subject to inherent uncertainties, risks and changes in circumstances that are difficult to predict. As a result, actual results could differ materially from those indicated in these forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially include global political, economic, business, competitive, market, regulatory and other factors and risks, such as: the impact of macroeconomic conditions and whether industry trends we have identified develop as anticipated, including the future impacts of the novel coronavirus disease (“COVID-19”) outbreak and measures taken in response thereto for which future developments are highly uncertain and difficult to predict; retaining existing partners and attracting new partners, concentration of our revenue in a small number of partners, and promotion and support of our products by our partners; cyber-attacks or other security breaches; disruptions in the operations of our and our outsourced partners' computer systems and data centers; the financial performance of our partners; the sufficiency of our allowance for credit losses and the accuracy of the assumptions or estimates used in preparing our financial statements, including those related to the CECL accounting guidance; higher borrowing costs and adverse financial market conditions impacting our funding and liquidity, and any reduction in our credit ratings; our ability to grow our deposits in the future; damage to our reputation; our ability to securitize our loan receivables, occurrence of an early amortization of our securitization facilities, loss of the right to service or subservice our securitized loan receivables, and lower payment rates on our securitized loan receivables; changes in market interest rates and the impact of any margin compression; effectiveness of our risk management processes and procedures, reliance on models which may be inaccurate or misinterpreted, our ability to manage our credit risk; our ability to offset increases in our costs in retailer share arrangements; competition in the consumer finance industry; our concentration in the U.S. consumer credit market; our ability to successfully develop and commercialize new or enhanced products and services; our ability to realize the value of acquisitions and strategic investments; reductions in interchange fees; fraudulent activity; failure of third-parties to provide various services that are important to our operations; international risks and compliance and regulatory risks and costs associated with international operations; alleged infringement of intellectual property rights of others and our ability to protect our intellectual property; litigation and regulatory actions; our ability to attract, retain and motivate key officers and employees; tax legislation initiatives or challenges to our tax positions and/or interpretations, and state sales tax rules and regulations; regulation, supervision, examination and enforcement of our business by governmental authorities, the impact of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”) and other legislative and regulatory developments and the impact of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau's (the “CFPB”) regulation of our business; impact of capital adequacy rules and liquidity requirements; restrictions that limit our ability to pay dividends and repurchase our common stock, and restrictions that limit the Bank’s ability to pay dividends to us; regulations relating to privacy, information security and data protection; use of third-party vendors and ongoing third-party business relationships; and failure to comply with anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism financing laws.
For the reasons described above, we caution you against relying on any forward-looking statements, which should also be read in conjunction with the other cautionary statements that are included elsewhere in this report and in our public filings, including under the heading “Risk Factors Relating to Our Business” and “Risk Factors Relating to Regulation” in our 2021 Form 10-K. You should not consider any list of such factors to be an exhaustive statement of all of the risks, uncertainties, or potentially inaccurate assumptions that could cause our current expectations or beliefs to change. Further, any forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which it is made, and we undertake no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statement to reflect events or circumstances after the date on which the statement is made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events, except as otherwise may be required by law.
PART I. FINANCIAL INFORMATION
ITEM 2. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our condensed consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this quarterly report and in our 2021 Form 10-K. The discussion below contains forward-looking statements that are based upon current expectations and are subject to uncertainty and changes in circumstances. Actual results may differ materially from these expectations. See “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.”
Introduction and Business Overview
____________________________________________________________________________________________
We are a premier consumer financial services company delivering one of the industry's most complete, digitally-enabled product suites. Our experience, expertise and scale encompass a broad spectrum of industries including digital, health and wellness, retail, telecommunications, home, auto, powersports, pet and more. We have an established and diverse group of national and regional retailers, local merchants, manufacturers, buying groups, industry associations and healthcare service providers, which we refer to as our “partners.” For the three months ended March 31, 2022, we financed $40.5 billion of purchase volume and had 70.1 million average active accounts, and at March 31, 2022, we had $78.9 billion of loan receivables.
We offer our credit products primarily through our wholly-owned subsidiary, the Bank. In addition, through the Bank, we offer, directly to retail, affinity relationships and commercial customers, a range of deposit products insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”), including certificates of deposit, individual retirement accounts (“IRAs”), money market accounts, savings accounts and sweep and affinity deposits. We also take deposits at the Bank through third-party securities brokerage firms that offer our FDIC-insured deposit products to their customers. We have significantly expanded our online direct banking operations in recent years and our deposit base serves as a source of stable and diversified low cost funding for our credit activities. At March 31, 2022, we had $63.6 billion in deposits, which represented 83% of our total funding sources.
Our Sales Platforms
_________________________________________________________________
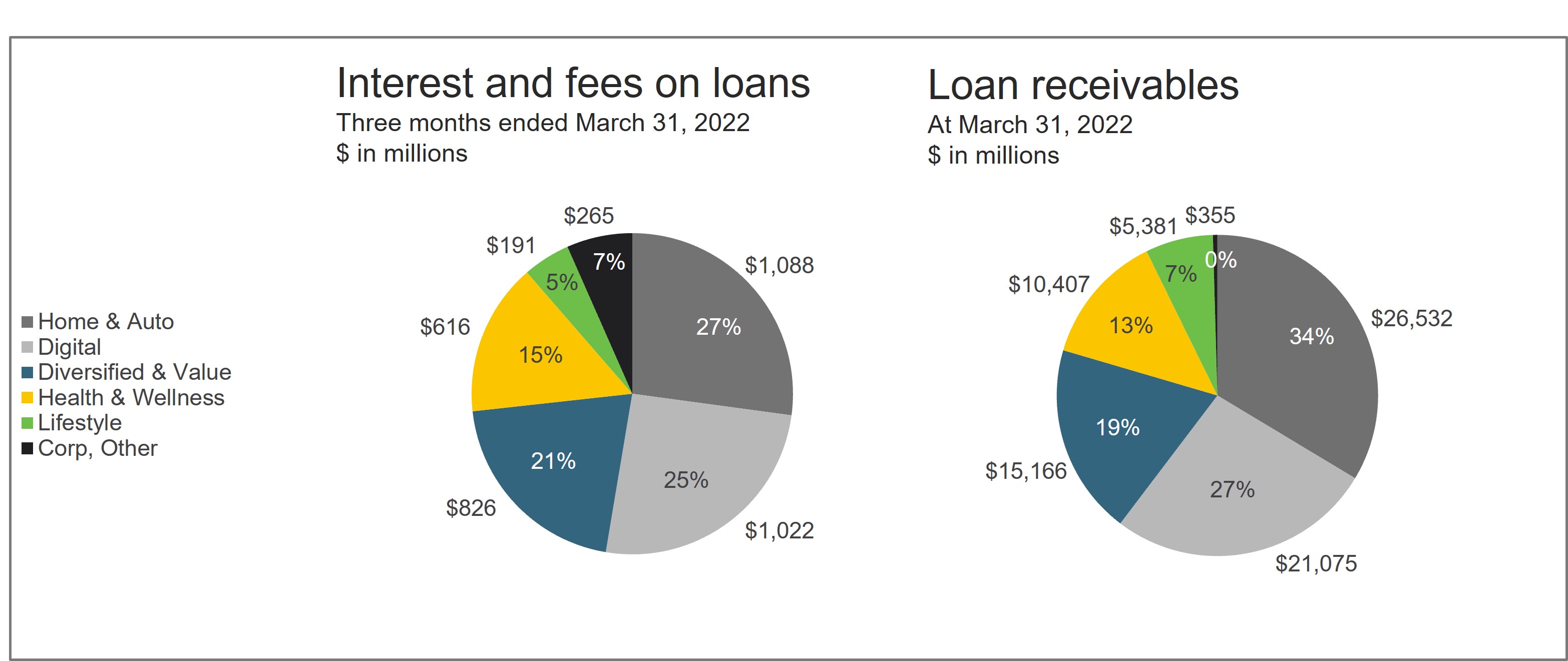
We conduct our operations through a single business segment. Profitability and expenses, including funding costs, credit losses and operating expenses, are managed for the business as a whole. Substantially all of our revenue activities are within the United States. We primarily manage our credit products through five sales platforms (Home & Auto, Digital, Diversified & Value, Health & Wellness and Lifestyle). Those platforms are organized by the types of partners we work with, and are measured on interest and fees on loans, loan receivables, active accounts and other sales metrics.
Home & Auto
Our Home & Auto sales platform provides comprehensive payments and financing solutions with integrated in-store and digital experiences through a broad network of partners and merchants providing home and automotive merchandise and services, as well as our Synchrony Car Care network and Synchrony HOME credit card offering. Our Home & Auto sales platform partners include a wide range of key retailers in the home improvement, furniture, bedding, appliance and electronics industry, such as Ashley HomeStores LTD, Lowe's, and Mattress Firm, as well as automotive merchandise and services, such as Chevron and Discount Tire. In addition, we also have program agreements with buying groups, manufacturers and industry associations, such as Nationwide Marketing Group and the Home Furnishings Association.
Digital
Our Digital sales platform provides comprehensive payments and financing solutions with integrated digital experiences through partners and merchants who primarily engage with their consumers through digital channels. Our Digital sales platform includes key partners delivering digital payment solutions, such as PayPal, including our Venmo program, online marketplaces, such as Amazon and eBay, and digital-first brands and merchants, such as Verizon, the Qurate brands, and Fanatics.
Diversified & Value
Our Diversified & Value sales platform provides comprehensive payments and financing solutions with integrated in-store and digital experiences through large retail partners who deliver everyday value to consumers shopping for daily needs or important life moments. Our Diversified & Value sales platform is comprised of five large retail partners: Belk, Fleet Farm, JCPenney, Sam's Club and TJX Companies, Inc.
Health & Wellness
Our Health & Wellness sales platform provides comprehensive healthcare payments and financing solutions, through a network of providers and health systems, for those seeking health and wellness care for themselves, their families and their pets, and includes key brands such as CareCredit and Pets Best, as well as partners such as Walgreens.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle provides comprehensive payments and financing solutions with integrated in-store and digital experiences through partners and merchants who offer merchandise in power sports, outdoor power equipment, and other industries such as sporting goods, apparel, jewelry and music. Our Lifestyle sales platform partners includes a wide range of key retailers in the apparel, specialty retail, outdoor, music and luxury industry, such as
American Eagle, Dick's Sporting Goods, Guitar Center, Polaris and Pandora.
Corp, Other
Corp, Other includes activity and balances related to certain program agreements with retail partners and merchants that will not be renewed beyond their current expiry date and certain programs that were previously terminated, which are not managed within the five sales platforms discussed above, and primarily includes amounts associated with our program agreements with Gap Inc. and BP which are scheduled to expire in the second quarter of 2022. Corp, Other also includes amounts related to changes in the fair value of equity investments and realized gains or losses associated with the sale of investments.
Our Credit Products
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Through our sales platforms, we offer three principal types of credit products: credit cards, commercial credit products and consumer installment loans. We also offer a debt cancellation product.
The following table sets forth each credit product by type and indicates the percentage of our total loan receivables that are under standard terms only or pursuant to a promotional financing offer at March 31, 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Promotional Offer | | |
| Credit Product | Standard Terms Only | | Deferred Interest | | Other Promotional | | Total |
| Credit cards | 57.5 | % | | 20.6 | % | | 16.4 | % | | 94.5 | % |
| Commercial credit products | 1.9 | | | — | | | — | | | 1.9 | |
| Consumer installment loans | 0.1 | | | 0.1 | | | 3.3 | | | 3.5 | |
| Other | 0.1 | | | — | | | — | | | 0.1 | |
| Total | 59.6 | % | | 20.7 | % | | 19.7 | % | | 100.0 | % |
Credit Cards
We offer the following principal types of credit cards:
•Private Label Credit Cards. Private label credit cards are partner-branded credit cards (e.g., Lowe’s or Amazon) or program-branded credit cards (e.g., Synchrony Car Care or CareCredit) that are used primarily for the purchase of goods and services from the partner or within the program network. In addition, in some cases, cardholders may be permitted to access their credit card accounts for cash advances. Credit under our private label credit cards typically is extended either on standard terms only or pursuant to a promotional financing offer.
•Dual Cards and General Purpose Co-Branded Cards. Our patented Dual Cards are credit cards that function as private label credit cards when used to purchase goods and services from our partners, and as general purpose credit cards when used to make purchases from other retailers wherever cards from those card networks are accepted or for cash advance transactions. We also offer general purpose co-branded credit cards that do not function as private label credit cards, as well as a Synchrony-branded general purpose credit card. Dual Cards and general purpose co-branded credit cards are offered across all of our sales platforms and credit is typically extended on standard terms only. We offer either Dual Cards or general purpose co-branded credit cards through 21 credit partners, of which the majority are Dual Cards, as well as our CareCredit Dual Card. Consumer Dual Cards and Co-Branded cards totaled 25% of our total loan receivables portfolio, including held for sale, at March 31, 2022.
Commercial Credit Products
We offer private label cards and Dual Cards for commercial customers that are similar to our consumer offerings. We also offer a commercial pay-in-full accounts receivable product to a wide range of business customers.
Installment Loans
We originate installment loans to consumers (and a limited number of commercial customers) in the United States, primarily in the power products market (motorcycles, ATVs and lawn and garden), as well as through our various SetPay installment products (such as our SetPay Pay in 4 product for short-term loans). Installment loans are closed-end credit accounts where the customer pays down the outstanding balance in installments. Installment loans are generally assessed periodic finance charges using fixed interest rates.
Business Trends and Conditions
____________________________________________________________________________________________
We believe our business and results of operations will be impacted in the future by various trends and conditions. For a discussion of certain trends and conditions, see “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Business Trends and Conditions” in our 2021 Form 10-K. For a discussion of how certain trends and conditions impacted the three months ended March 31, 2022, see “—Results of Operations.”
Seasonality
____________________________________________________________________________________________
We experience fluctuations in transaction volumes and the level of loan receivables as a result of higher seasonal consumer spending and payment patterns that typically result in an increase of loan receivables from August through a peak in late December, with reductions in loan receivables occurring over the first and second quarters of the following year as customers pay their balances down.
The seasonal impact to transaction volumes and the loan receivables balance typically results in fluctuations in our results of operations, delinquency metrics and the allowance for credit losses as a percentage of total loan receivables between quarterly periods.
In addition to the seasonal variance in loan receivables discussed above, we also typically experience a seasonal increase in delinquency rates and delinquent loan receivables balances during the third and fourth quarters of each year due to lower customer payment rates resulting in higher net charge-off rates in the first and second quarters. Our delinquency rates and delinquent loan receivables balances typically decrease during the subsequent first and second quarters as customers begin to pay down their loan balances and return to current status resulting in lower net charge-off rates in the third and fourth quarters. Because customers who were delinquent during the fourth quarter of a calendar year have a higher probability of returning to current status when compared to customers who are delinquent at the end of each of our interim reporting periods, we expect that a higher proportion of delinquent accounts outstanding at an interim period end will result in charge-offs, as compared to delinquent accounts outstanding at a year end. Consistent with this historical experience, we generally experience a higher allowance for credit losses as a percentage of total loan receivables at the end of an interim period, as compared to the end of a calendar year. In addition, despite improving credit metrics such as declining past due amounts, we may experience an increase in our allowance for credit losses at an interim period end compared to the prior year end, reflecting these same seasonal trends.
The seasonal trends discussed above are most evident between the fourth quarter and the first quarter of the following year. In addition to these seasonal trends, we continue to experience improvements in customer payment behavior, which include the effects of governmental stimulus actions, industry-wide forbearance measures and elevated consumer savings. Customer payments as a percentage of beginning-of-period loan receivables for the three months ended March 31, 2022 were approximately 45 basis points higher than the prior year period, and are significantly elevated compared to historical averages.
Loan receivables decreased by $1.8 billion, or 2.3% to $78.9 billion at March 31, 2022 compared to $80.7 billion at December 31, 2021, and our allowance for credit losses as a percentage of total loan receivables increased to 10.96% at March 31, 2022, from 10.76% at December 31, 2021, reflecting the seasonal trends discussed above. Past due balances increased to $2.2 billion at March 31, 2022 from $2.1 billion at December 31, 2021 as the effects from some moderation in elevated payment rates exceeded the impact of the seasonal trends we experienced.
Results of Operations
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Highlights for the Three Months Ended March 31, 2022
Below are highlights of our performance for the three months ended March 31, 2022 compared to the three months ended March 31, 2021, as applicable, except as otherwise noted.
•Net earnings decreased to $932 million from $1.0 billion. The decrease in the three months ended March 31, 2022 was primarily driven by increases in provision for credit losses, retailer share arrangements and other expense, partially offset by higher net interest income.
•Loan receivables increased to $78.9 billion at March 31, 2022 compared to $76.9 billion at March 31, 2021, driven by strong purchase volume growth, partially offset by the reclassification of loan receivables associated with the Gap Inc and BP portfolios to loan receivables held for sale. Loan receivables held for sale at March 31, 2022 were $4.0 billion. Excluding the impact of the reclassifications of these portfolios to loan receivables held for sale, loan receivables increased 7.9% reflecting strong purchase volume growth of 16.5%, partially offset by elevated customer payment rates.
•Net interest income increased 10.2% to $3.8 billion for the three months ended March 31, 2022. Interest and fees on loans increased by $276 million, or 7.4%, driven by growth in average loan receivables and interest expense decreased by $70 million, or 23.1%, primarily attributed to lower benchmark rates and lower funding liabilities.
•Retailer share arrangements increased 11.6% to $1.1 billion for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily due to continued strong program performance.
•Over-30 day loan delinquencies as a percentage of period-end loan receivables decreased 5 basis points to 2.78% at March 31, 2022. Excluding amounts related to the held for sale portfolios, the decrease compared to the prior year was approximately 15 basis points. The net charge-off rate decreased 89 basis points to 2.73% for the three months ended March 31, 2022.
•Provision for credit losses increased by $187 million, or 56.0% for the three months ended March 31, 2022 primarily driven by a lower reserve release compared to prior year, partially offset by lower net charge-offs. The reduction in reserves for credit losses in the current year included a $29 million reserve reduction related to the held for sale portfolios. Our allowance coverage ratio (allowance for credit losses as a percent of period-end loan receivables) decreased to 10.96% at March 31, 2022, as compared to 12.88% at March 31, 2021.
•Other expense increased by $107 million, or 11.5% for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily driven by higher employee, marketing and business development and technology costs.
•At March 31, 2022, deposits represented 83% of our total funding sources. Total deposits increased by 2.1% to $63.6 billion at March 31, 2022, compared to December 31, 2021.
•During the three months ended March 31, 2022, we declared and paid cash dividends on our Series A 5.625% non-cumulative preferred stock of $14.06 per share, or $10 million.
•In April 2022, we announced that our Board approved an incremental share repurchase authorization of $2.8 billion through June 2023 and plans to increase our quarterly dividend by 5% to $0.23 per common share commencing in the third quarter of 2022. During the three months ended March 31, 2022, we repurchased $967 million of our outstanding common stock, and declared and paid cash dividends of $0.22 per share, or $114 million. Inclusive of the $251 million of remaining authorized share repurchase capacity at March 31, 2022 we have a total share repurchase authorization of $3.1 billion. For more information, see “Capital—Dividend and Share Repurchases.”
2022 Partner Agreements
During the quarter ended March 31, 2022, we continued to expand and diversify our portfolio with the addition or renewal of more than 15 partners, which included the following:
•In our Home & Auto sales platform, we announced our new partnership with Furnitureland South and extended our agreements with Cardi's, Generac Power Systems, Mattress Warehouse, NAPA AutoCare and New South Window Solutions.
•In our Health & Wellness sales platform, we expanded our network through our new partnerships with Buffalo Veterinary Group and Service Corporation International and extended our agreements with Encore Vet Group.
•In our Lifestyle sales platform, we extended our program agreements with Guitar Center and Reeds.
Summary Earnings
The following table sets forth our results of operations for the periods indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Interest income | $ | 4,022 | | | $ | 3,742 | | | | | |
| Interest expense | 233 | | | 303 | | | | | |
| Net interest income | 3,789 | | | 3,439 | | | | | |
| Retailer share arrangements | (1,104) | | | (989) | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Provision for credit losses | 521 | | | 334 | | | | | |
| Net interest income, after retailer share arrangements and provision for credit losses | 2,164 | | | 2,116 | | | | | |
| Other income | 108 | | | 131 | | | | | |
| Other expense | 1,039 | | | 932 | | | | | |
| Earnings before provision for income taxes | 1,233 | | | 1,315 | | | | | |
| Provision for income taxes | 301 | | | 290 | | | | | |
| Net earnings | $ | 932 | | | $ | 1,025 | | | | | |
| Net earnings available to common stockholders | $ | 922 | | | $ | 1,014 | | | | | |
Other Financial and Statistical Data
The following table sets forth certain other financial and statistical data for the periods indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At and for the | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Financial Position Data (Average): | | | | | | | |
| Loan receivables, including held for sale | $ | 82,747 | | | $ | 78,358 | | | | | |
| Total assets | $ | 95,556 | | | $ | 96,455 | | | | | |
| Deposits | $ | 62,688 | | | $ | 63,070 | | | | | |
| Borrowings | $ | 14,046 | | | $ | 15,659 | | | | | |
| Total equity | $ | 13,731 | | | $ | 13,071 | | | | | |
| Selected Performance Metrics: | | | | | | | |
Purchase volume(1)(2) | $ | 40,490 | | | $ | 34,749 | | | | | |
| Home & Auto | $ | 10,260 | | | $ | 9,337 | | | | | |
| Digital | $ | 11,196 | | | $ | 9,340 | | | | | |
| Diversified & Value | $ | 11,558 | | | $ | 9,220 | | | | | |
| Health & Wellness | $ | 3,107 | | | $ | 2,648 | | | | | |
| Lifestyle | $ | 1,195 | | | $ | 1,154 | | | | | |
| Corp, Other | $ | 3,174 | | | $ | 3,050 | | | | | |
Average active accounts (in thousands)(2)(3) | 70,127 | | | 66,280 | | | | | |
Net interest margin(4) | 15.80 | % | | 13.98 | % | | | | |
| Net charge-offs | $ | 558 | | | $ | 699 | | | | | |
| Net charge-offs as a % of average loan receivables, including held for sale | 2.73 | % | | 3.62 | % | | | | |
Allowance coverage ratio(5) | 10.96 | % | | 12.88 | % | | | | |
Return on assets(6) | 4.0 | % | | 4.3 | % | | | | |
Return on equity(7) | 27.5 | % | | 31.8 | % | | | | |
Equity to assets(8) | 14.37 | % | | 13.55 | % | | | | |
| Other expense as a % of average loan receivables, including held for sale | 5.09 | % | | 4.82 | % | | | | |
Efficiency ratio(9) | 37.2 | % | | 36.1 | % | | | | |
| Effective income tax rate | 24.4 | % | | 22.1 | % | | | | |
| Selected Period-End Data: | | | | | | | |
| Loan receivables | $ | 78,916 | | | $ | 76,858 | | | | | |
| Allowance for credit losses | $ | 8,651 | | | $ | 9,901 | | | | | |
30+ days past due as a % of period-end loan receivables(10) | 2.78 | % | | 2.83 | % | | | | |
90+ days past due as a % of period-end loan receivables(10) | 1.30 | % | | 1.52 | % | | | | |
Total active accounts (in thousands)(2)(3) | 69,122 | | | 65,219 | | | | | |
______________________(1)Purchase volume, or net credit sales, represents the aggregate amount of charges incurred on credit cards or other credit product accounts less returns during the period.
(2)Includes activity and accounts associated with loan receivables held for sale.
(3)Active accounts represent credit card or installment loan accounts on which there has been a purchase, payment or outstanding balance in the current month.
(4)Net interest margin represents net interest income divided by average interest-earning assets.
(5)Allowance coverage ratio represents allowance for credit losses divided by total period-end loan receivables.
(6)Return on assets represents net earnings as a percentage of average total assets.
(7)Return on equity represents net earnings as a percentage of average total equity.
(8)Equity to assets represents average total equity as a percentage of average total assets.
(9)Efficiency ratio represents (i) other expense, divided by (ii) sum of net interest income, plus other income, less retailer share arrangements.
(10)Based on customer statement-end balances extrapolated to the respective period-end date.
Average Balance Sheet
The following tables set forth information for the periods indicated regarding average balance sheet data, which are used in the discussion of interest income, interest expense and net interest income that follows.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| Three months ended March 31 ($ in millions) | Average
Balance | | Interest
Income /
Expense | | Average Yield / Rate(1) | | Average
Balance | | Interest
Income/
Expense | | Average Yield / Rate(1) | | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest-earning assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest-earning cash and equivalents(2) | $ | 8,976 | | | $ | 5 | | | 0.23 | % | | $ | 14,610 | | | $ | 4 | | | 0.11 | % | | |
| Securities available for sale | 5,513 | | | 9 | | | 0.66 | % | | 6,772 | | | 6 | | | 0.36 | % | | |
Loan receivables, including held for sale(3): | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Credit cards | 78,564 | | | 3,913 | | | 20.20 | % | | 74,865 | | | 3,657 | | | 19.81 | % | | |
| Consumer installment loans | 2,682 | | | 66 | | | 9.98 | % | | 2,219 | | | 53 | | | 9.69 | % | | |
| Commercial credit products | 1,434 | | | 28 | | | 7.92 | % | | 1,231 | | | 21 | | | 6.92 | % | | |
| Other | 67 | | | 1 | | | NM | | 43 | | | 1 | | | NM | | |
| Total loan receivables, including held for sale | 82,747 | | | 4,008 | | | 19.64 | % | | 78,358 | | | 3,732 | | | 19.32 | % | | |
| Total interest-earning assets | 97,236 | | | 4,022 | | | 16.78 | % | | 99,740 | | | 3,742 | | | 15.22 | % | | |
| Non-interest-earning assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and due from banks | 1,626 | | | | | | | 1,635 | | | | | | | |
| Allowance for credit losses | (8,675) | | | | | | | (10,225) | | | | | | | |
| Other assets | 5,369 | | | | | | | 5,305 | | | | | | | |
| Total non-interest-earning assets | (1,680) | | | | | | | (3,285) | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | $ | 95,556 | | | | | | | $ | 96,455 | | | | | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest-bearing liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest-bearing deposit accounts | $ | 62,314 | | | $ | 127 | | | 0.83 | % | | $ | 62,724 | | | $ | 170 | | | 1.10 | % | | |
| Borrowings of consolidated securitization entities | 6,827 | | | 33 | | | 1.96 | % | | 7,694 | | | 51 | | | 2.69 | % | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Senior unsecured notes | 7,219 | | | 73 | | | 4.10 | % | | 7,965 | | | 82 | | | 4.18 | % | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total interest-bearing liabilities | 76,360 | | | 233 | | | 1.24 | % | | 78,383 | | | 303 | | | 1.57 | % | | |
| Non-interest-bearing liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-interest-bearing deposit accounts | 374 | | | | | | | 346 | | | | | | | |
| Other liabilities | 5,091 | | | | | | | 4,655 | | | | | | | |
| Total non-interest-bearing liabilities | 5,465 | | | | | | | 5,001 | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities | 81,825 | | | | | | | 83,384 | | | | | | | |
| Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total equity | 13,731 | | | | | | | 13,071 | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 95,556 | | | | | | | $ | 96,455 | | | | | | | |
Interest rate spread(4) | | | | | 15.54 | % | | | | | | 13.65 | % | | |
| Net interest income | | | $ | 3,789 | | | | | | | $ | 3,439 | | | | | |
Net interest margin(5) | | | | | 15.80 | % | | | | | | 13.98 | % | | |
_______________________
(1)Average yields/rates are based on total interest income/expense over average balances.
(2)Includes average restricted cash balances of $614 million and $423 million for the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
(3)Interest income on loan receivables includes fees on loans of $652 million and $514 million for the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
(4)Interest rate spread represents the difference between the yield on total interest-earning assets and the rate on total interest-bearing liabilities.
(5)Net interest margin represents net interest income divided by average total interest-earning assets.
For a summary description of the composition of our key line items included in our Statements of Earnings, see Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations in our 2021 Form 10-K.
Interest Income
Interest income increased by $280 million, or 7.5%. The increase in the three months ended March 31, 2022 was primarily driven by increases in interest and fees on loans attributed to growth in average loan receivables, including held for sale.
Average interest-earning assets
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31 ($ in millions) | 2022 | | % | | 2021 | | % | | | | |
| Loan receivables, including held for sale | $ | 82,747 | | | 85.1 | % | | $ | 78,358 | | | 78.6 | % | | | | |
| Liquidity portfolio and other | 14,489 | | | 14.9 | % | | 21,382 | | | 21.4 | % | | | | |
| Total average interest-earning assets | $ | 97,236 | | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 99,740 | | | 100.0 | % | | | | |
Average loan receivables, including held for sale, increased by 5.6% for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily driven by growth in purchase volume of 16.5%, partially offset by improvement in customer payment behavior. Customer payments as a percentage of beginning-of-period loan receivables for the three months ended March 31, 2022 were approximately 45 basis points higher than the prior year period.
Yield on average interest-earning assets
The yield on average interest-earning assets increased for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily due to an increase in the percentage of interest-earning assets attributable to loan receivables, as well as an increase in the yield on average loan receivables. The increase in loan receivable yield was 32 basis points to 19.6% for the three months ended March 31, 2022.
Interest Expense
Interest expense decreased by $70 million, or 23.1%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily attributed to lower benchmark interest rates and lower funding liabilities. Our cost of funds decreased to 1.24% for the three months ended March 31, 2022, compared to 1.57% for the three months ended March 31, 2021.
Average interest-bearing liabilities
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31 ($ in millions) | 2022 | | % | | 2021 | | % | | | | |
| Interest-bearing deposit accounts | $ | 62,314 | | | 81.6 | % | | $ | 62,724 | | | 80.0 | % | | | | |
| Borrowings of consolidated securitization entities | 6,827 | | | 8.9 | % | | 7,694 | | | 9.8 | % | | | | |
| Senior unsecured notes | 7,219 | | | 9.5 | % | | 7,965 | | | 10.2 | % | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total average interest-bearing liabilities | $ | 76,360 | | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 78,383 | | | 100.0 | % | | | | |
Net Interest Income
Net interest income increased by $350 million, or 10.2%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022, resulting from the changes in interest income and interest expense discussed above.
Retailer Share Arrangements
Retailer share arrangements increased by $115 million, or 11.6%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily due to continued strong program performance.
Provision for Credit Losses
Provision for credit losses increased by $187 million, or 56.0%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily driven by a lower reserve release in the current year, partially offset by lower net charge-offs. The reductions in reserves for credit losses for the three months ended March 31, 2022 were $37 million, including a $29 million reserve reduction related to the held for sale portfolios.
Other Income
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Interchange revenue | $ | 230 | | | $ | 171 | | | | | |
| Debt cancellation fees | 89 | | | 69 | | | | | |
| Loyalty programs | (258) | | | (179) | | | | | |
| Other | 47 | | | 70 | | | | | |
| Total other income | $ | 108 | | | $ | 131 | | | | | |
Other income decreased by $23 million, or 17.6%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022 primarily driven by higher loyalty program costs associated with purchase volume growth, and lower investment gains.
Other Expense
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Employee costs | $ | 402 | | | $ | 364 | | | | | |
| Professional fees | 210 | | | 190 | | | | | |
| Marketing and business development | 116 | | | 95 | | | | | |
| Information processing | 145 | | | 131 | | | | | |
| Other | 166 | | | 152 | | | | | |
| Total other expense | $ | 1,039 | | | $ | 932 | | | | | |
Other expense increased by $107 million, or 11.5%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily driven by increases in employee costs, marketing and business development, professional fees and information processing.
The increase in employee costs was primarily attributable to increase in non-exempt headcount driven by growth and insourcing, higher hourly wages and other compensation adjustments. The increase in marketing and business development was primarily driven by higher contractual and discretionary marketing investments. The increase in professional fees and information processing costs was primarily due to higher technology investments and purchase volume.
Provision for Income Taxes
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Effective tax rate | 24.4 | % | | 22.1 | % | | | | |
| Provision for income taxes | $ | 301 | | | $ | 290 | | | | | |
The effective tax rate for the three months ended March 31, 2022 increased compared to the same period in the prior year primarily due to the resolution of certain tax matters in the prior period. For both periods presented, the effective tax rate differs from the applicable U.S. federal statutory tax rate primarily due to state income taxes.
Platform Analysis
As discussed above under “—Our Sales Platforms,” we offer our credit products primarily through five sales platforms (Home & Auto, Digital, Diversified & Value, Health & Wellness and Lifestyle), which management measures based on their revenue-generating activities. The following is a discussion of certain supplemental information for the three months ended March 31, 2022, for each of our five sales platforms and Corp, Other.
Home & Auto
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Purchase volume | $ | 10,260 | | | $ | 9,337 | | | | | |
| Period-end loan receivables | $ | 26,532 | | | $ | 24,942 | | | | | |
| Average loan receivables, including held for sale | $ | 26,406 | | | $ | 25,273 | | | | | |
| Average active accounts (in thousands) | 17,473 | | | 17,149 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Interest and fees on loans | $ | 1,088 | | | $ | 1,036 | | | | | |
| Other income | $ | 21 | | | $ | 17 | | | | | |
Home & Auto interest and fees on loans increased by $52 million, or 5.0%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022 primarily driven by growth in average loan receivables. The growth in average loan receivables reflected purchase volume growth of 9.9%, partially offset by elevated customer payment rates.
Digital
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Purchase volume | $ | 11,196 | | | $ | 9,340 | | | | | |
| Period-end loan receivables | $ | 21,075 | | | $ | 18,907 | | | | | |
| Average loan receivables, including held for sale | $ | 21,160 | | | $ | 19,437 | | | | | |
| Average active accounts (in thousands) | 19,000 | | | 17,318 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Interest and fees on loans | $ | 1,022 | | | $ | 903 | | | | | |
| Other income | $ | (12) | | | $ | (12) | | | | | |
Digital interest and fees on loans increased by $119 million, or 13.2%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily driven by growth in average loan receivables. The growth in average loan receivables reflected purchase volume growth of 19.9% and average active account growth of 9.7%, partially offset by elevated customer payment rates.
Diversified & Value
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Purchase volume | $ | 11,558 | | | $ | 9,220 | | | | | |
| Period-end loan receivables | $ | 15,166 | | | $ | 14,217 | | | | | |
| Average loan receivables, including held for sale | $ | 15,128 | | | $ | 14,574 | | | | | |
| Average active accounts (in thousands) | 19,201 | | | 17,457 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Interest and fees on loans | $ | 826 | | | $ | 789 | | | | | |
| Other income | $ | (9) | | | $ | 5 | | | | | |
Diversified & Value interest and fees on loans increased by $37 million, or 4.7%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily driven by growth in average loan receivables. The growth in average loan receivables reflected purchase volume growth of 25.4% and average active account growth of 10.0%, partially offset by elevated customer payment rates.
Other income decreased by $14 million, for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily driven by higher program loyalty costs.
Health & Wellness
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Purchase volume | $ | 3,107 | | | $ | 2,648 | | | | | |
| Period-end loan receivables | $ | 10,407 | | | $ | 9,317 | | | | | |
| Average loan receivables, including held for sale | $ | 10,251 | | | $ | 9,442 | | | | | |
| Average active accounts (in thousands) | 6,027 | | | 5,706 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Interest and fees on loans | $ | 616 | | | $ | 558 | | | | | |
| Other income | $ | 53 | | | $ | 40 | | | | | |
Health & Wellness interest and fees on loans increased by $58 million, or 10.4%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily driven by growth in average loan receivables. The growth in average loan receivables reflected strength across the network, particularly in Dental as patient volume increased compared to prior year. Purchase volume increased 17.3% and average active accounts increased 5.6%. The impacts from these increases were partially offset by elevated payment rates.
Other income increased by $13 million, or 32.5%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily due to commission fees earned by Pets Best.
Lifestyle
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Purchase volume | $ | 1,195 | | | $ | 1,154 | | | | | |
| Period-end loan receivables | $ | 5,381 | | | $ | 4,988 | | | | | |
| Average loan receivables, including held for sale | $ | 5,379 | | | $ | 5,003 | | | | | |
| Average active accounts (in thousands) | 2,582 | | | 2,573 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Interest and fees on loans | $ | 191 | | | $ | 181 | | | | | |
| Other income | $ | 6 | | | $ | 5 | | | | | |
Lifestyle interest and fees on loans increased by $10 million, or 5.5%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily driven by growth in average loan receivables. The growth in average loan receivables reflected purchase volume growth of 3.6% which was driven by strength in our Music and Specialty retail partners, partially offset by comparison to strong growth in Power in the prior year.
Corp, Other
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Purchase volume | $ | 3,174 | | | $ | 3,050 | | | | | |
| Period-end loan receivables | $ | 355 | | | $ | 4,487 | | | | | |
| Average loan receivables, including held for sale | $ | 4,423 | | | $ | 4,629 | | | | | |
| Average active accounts (in thousands) | 5,844 | | | 6,077 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Interest and fees on loans | $ | 265 | | | $ | 265 | | | | | |
| Other income | $ | 49 | | | $ | 76 | | | | | |
Corp, Other interest and fees on loans remained flat for the three months ended March 31, 2022.
Other income decreased by $27.0 million, or 35.5%, for the three months ended March 31, 2022, primarily due to lower investment gains.
Loan Receivables
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Loan receivables are our largest category of assets and represent our primary source of revenue. The following discussion provides supplemental information regarding our loan receivables portfolio. See Note 2. Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies and Note 4. Loan Receivables and Allowance for Credit Losses to our condensed consolidated financial statements for additional information related to our loan receivables, including troubled debt restructurings (“TDRs”).
The following table sets forth the composition of our loan receivables portfolio by product type at the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | At March 31, 2022 | | (%) | | At December 31, 2021 | | (%) |
| Loans | | | | | |
| Credit cards | $ | 74,596 | | | 94.5 | % | | $ | 76,628 | | | 94.9 | % |
| Consumer installment loans | 2,719 | | | 3.5 | % | | 2,675 | | | 3.4 | |
| Commercial credit products | 1,530 | | | 1.9 | % | | 1,372 | | | 1.7 | |
| Other | 71 | | | 0.1 | % | | 65 | | | — | |
| Total loans | $ | 78,916 | | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 80,740 | | | 100.0 | % |
Loan receivables decreased 2.3% to $78.9 billion at March 31, 2022 compared to December 31, 2021, primarily driven by the seasonality of our business, partially offset by strong purchase volume growth and some moderation in customer payment rates.
Loan receivables increased 2.7% to $78.9 billion at March 31, 2022 compared to $76.9 billion at March 31, 2021, primarily due to strong purchase volume growth, partially offset by the reclassification of loan receivables associated with the Gap Inc. and BP portfolios to loan receivables held for sale. Loan receivables held for sale totaled $4.0 billion at March 31, 2022, and we expect conveyance of both portfolios to occur, subject to customary closing conditions, in the second quarter of 2022. Excluding the impact of the reclassification of these portfolios to loan receivables held for sale, loan receivables increased 7.9% reflecting strong purchase volume growth, partially offset by elevated customer payment rates.
Our loan receivables portfolio had the following geographic concentration at March 31, 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | Loan Receivables
Outstanding | | % of Total Loan
Receivables
Outstanding |
| State |
| Texas | $ | 8,490 | | | 10.8 | % |
| California | $ | 8,172 | | | 10.4 | % |
| Florida | $ | 7,198 | | | 9.1 | % |
| New York | $ | 4,030 | | | 5.1 | % |
| North Carolina | $ | 3,256 | | | 4.1 | % |
Delinquencies
Over-30 day loan delinquencies as a percentage of period-end loan receivables decreased to 2.78% at March 31, 2022 from 2.83% at March 31, 2021, and increased from 2.62% at December 31, 2021. The decrease compared to the prior year period was primarily driven by improvements in customer payment behavior, partially offset by the effects of the reclassification of loan receivables related to the Gap Inc. and BP portfolios to loan receivables held for sale. When excluding amounts related to held for sale portfolios from both current year and prior year periods, over-30 day loan delinquencies at March 31, 2022 declined approximately 15 basis points compared to March 31, 2021. The current quarter increase as compared to December 31, 2021 was primarily driven by some moderation in customer payment rates, partially offset by the seasonality of our business.
Net Charge-Offs
Net charge-offs consist of the unpaid principal balance of loans held for investment that we determine are uncollectible, net of recovered amounts. We exclude accrued and unpaid finance charges and fees and third-party fraud losses from charge-offs. Charged-off and recovered finance charges and fees are included in interest and fees on loans while third-party fraud losses are included in other expense. Charge-offs are recorded as a reduction to the allowance for credit losses and subsequent recoveries of previously charged-off amounts are credited to the allowance for credit losses. Costs incurred to recover charged-off loans are recorded as collection expense and included in other expense in our Condensed Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
The table below sets forth the net charge-offs and ratio of net charge-offs to average loan receivables, including held for sale, (“net charge-off rate”) for the periods indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Three months ended March 31, | | Three months ended March 31, | | | | |
| | | | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | | | | | Amount | | Rate | | Amount | | Rate | | | | |
| Credit cards | | | | | $ | 530 | | | 2.74 | % | | $ | 682 | | | 3.69 | % | | | | |
| Consumer installment loans | | | | | 17 | | | 2.57 | % | | 10 | | | 1.83 | % | | | | |
| Commercial credit products | | | | | 11 | | | 3.11 | % | | 7 | | | 2.64 | % | | | | |
| Other | | | | | — | | | — | % | | — | | | — | % | | | | |
| Total net charge-offs | | | | | $ | 558 | | | 2.73 | % | | $ | 699 | | | 3.62 | % | | | | |
Allowance for Credit Losses
The allowance for credit losses totaled $8.7 billion at March 31, 2022, compared to $8.7 billion at December 31, 2021 and $9.9 billion at March 31, 2021, and reflects our estimate of expected credit losses for the life of the loan receivables on our consolidated statement of financial position. Our allowance for credit losses as a percentage of total loan receivables increased to 10.96% at March 31, 2022, from 10.76% at December 31, 2021 and decreased from 12.88% at March 31, 2021.
The decrease compared to March 31, 2021 is primarily driven by improvements in customer payment behavior, which resulted in a reduction in our estimate of expected credit losses. The allowance for credit losses remained relatively flat compared to December 31, 2021 reflecting recent trends in customer payment behavior, partially offset by an uncertain macroeconomic environment.
Funding, Liquidity and Capital Resources
____________________________________________________________________________________________
We maintain a strong focus on liquidity and capital. Our funding, liquidity and capital policies are designed to ensure that our business has the liquidity and capital resources to support our daily operations, our business growth, our credit ratings and our regulatory and policy requirements, in a cost effective and prudent manner through expected and unexpected market environments.
Funding Sources
Our primary funding sources include cash from operations, deposits (direct and brokered deposits), securitized financings and senior unsecured notes.
The following table summarizes information concerning our funding sources during the periods indicated: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Three months ended March 31 ($ in millions) | Average
Balance | | % | | Average
Rate | | Average
Balance | | % | | Average
Rate |
Deposits(1) | $ | 62,314 | | | 81.6 | % | | 0.8 | % | | $ | 62,724 | | | 80.0 | % | | 1.1 | % |
| Securitized financings | 6,827 | | | 8.9 | | | 2.0 | | | 7,694 | | | 9.8 | | | 2.7 | |
| Senior unsecured notes | 7,219 | | | 9.5 | | | 4.1 | | | 7,965 | | | 10.2 | | | 4.2 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | $ | 76,360 | | | 100.0 | % | | 1.2 | % | | $ | 78,383 | | | 100.0 | % | | 1.6 | % |
______________________ (1)Excludes $374 million and $346 million average balance of non-interest-bearing deposits for the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Non-interest-bearing deposits comprise less than 10% of total deposits for the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021.
Deposits
We obtain deposits directly from retail, affinity relationships and commercial customers (“direct deposits”) or through third-party brokerage firms that offer our deposits to their customers (“brokered deposits”). At March 31, 2022, we had $52.5 billion in direct deposits and $11.1 billion in deposits originated through brokerage firms (including network deposit sweeps procured through a program arranger that channels brokerage account deposits to us). A key part of our liquidity plan and funding strategy is to continue to utilize our direct deposits base as a source of stable and diversified low-cost funding.
Our direct deposits include a range of FDIC-insured deposit products, including certificates of deposit, IRAs, money market accounts, savings accounts, sweep and affinity deposits.
Brokered deposits are primarily from retail customers of large brokerage firms. We have relationships with 10 brokers that offer our deposits through their networks. Our brokered deposits consist primarily of certificates of deposit that bear interest at a fixed rate. These deposits generally are not subject to early withdrawal.
Our ability to attract deposits is sensitive to, among other things, the interest rates we pay, and therefore, we bear funding risk if we fail to pay higher rates, or interest rate risk if we are required to pay higher rates, to retain existing deposits or attract new deposits. To mitigate these risks, our funding strategy includes a range of deposit products, and we seek to maintain access to multiple other funding sources, including securitized financings (including our undrawn committed capacity) and unsecured debt.
In December 2020, the FDIC issued a final rule to revise and clarify its framework for classifying deposits as brokered deposits, with full compliance with this rule required by January 1, 2022. In accordance with this final rule, deposits generated through certain sweep deposit relationships were reclassified from brokered to direct deposits in the first quarter of 2022.
The following table summarizes certain information regarding our interest-bearing deposits by type (all of which constitute U.S. deposits) for the periods indicated:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31 ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 |
Average
Balance | | % | | Average
Rate | | Average
Balance | | % | | Average
Rate |
| Direct deposits: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Certificates of deposit
(including IRA certificates of deposit) | $ | 20,226 | | | 32.5 | % | | 1.0 | % | | $ | 25,291 | | | 40.3 | % | | 1.5 | % |
| Savings, money market, and demand accounts | 31,097 | | | 49.9 | | | 0.5 | | | 26,806 | | | 42.8 | | | 0.5 | |
| Brokered deposits | 10,991 | | | 17.6 | | | 1.3 | | | 10,627 | | | 16.9 | | | 1.5 | |
| Total interest-bearing deposits | $ | 62,314 | | | 100.0 | % | | 0.8 | % | | $ | 62,724 | | | 100.0 | % | | 1.1 | % |
Our deposit liabilities provide funding with maturities ranging from one day to ten years. At March 31, 2022, the weighted average maturity of our interest-bearing time deposits was 1.0 years. See Note 7. Deposits to our condensed consolidated financial statements for more information on the maturities of our time deposits.
The following table summarizes deposits by contractual maturity at March 31, 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | 3 Months or
Less | | Over
3 Months
but within
6 Months | | Over
6 Months
but within
12 Months | | Over
12 Months | | Total |
U.S. deposits (less than FDIC insurance limit)(1)(2) | $ | 31,177 | | | $ | 2,829 | | | $ | 6,280 | | | $ | 9,278 | | | $ | 49,564 | |
U.S. deposits (in excess of FDIC insurance limit)(2) | | | | | | | | | |
| Direct deposits: | | | | | | | | | |
Certificates of deposit
(including IRA certificates of deposit) | 1,065 | | | 757 | | | 1,685 | | | 1,737 | | | 5,244 | |
| Savings, money market, and demand accounts | 8,767 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 8,767 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total | $ | 41,009 | | | $ | 3,586 | | | $ | 7,965 | | | $ | 11,015 | | | $ | 63,575 | |
______________________
(1)Includes brokered certificates of deposit for which underlying individual deposit balances are assumed to be less than $250,000.
(2)The standard deposit insurance amount is $250,000 per depositor, for each account ownership category. Deposits in excess of FDIC insurance limit presented above include partially uninsured accounts.
Securitized Financings
We access the asset-backed securitization market using the Synchrony Credit Card Master Note Trust (“SYNCT”) and the Synchrony Card Issuance Trust (“SYNIT”) through which we may issue asset-backed securities through both public transactions and private transactions funded by financial institutions and commercial paper conduits. In addition, we issue asset-backed securities in private transactions through the Synchrony Sales Finance Master Trust (“SFT”).
The following table summarizes expected contractual maturities of the investors’ interests in securitized financings, excluding debt premiums, discounts and issuance costs at March 31, 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | Less Than
One Year | | One Year
Through
Three
Years | | Four Years
Through
Five
Years | | After Five
Years | | Total |
| Scheduled maturities of long-term borrowings—owed to securitization investors: | | | | | | | | | |
SYNCT(1) | $ | 2,608 | | | $ | 1,382 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 3,990 | |
| SFT | 500 | | | 800 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,300 | |
SYNIT(1) | 850 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 850 | |
| Total long-term borrowings—owed to securitization investors | $ | 3,958 | | | $ | 2,182 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 6,140 | |
______________________
(1)Excludes any subordinated classes of SYNCT notes and SYNIT notes that we owned at March 31, 2022.
We retain exposure to the performance of trust assets through: (i) in the case of SYNCT, SFT and SYNIT, subordinated retained interests in the loan receivables transferred to the trust in excess of the principal amount of the notes for a given series that provide credit enhancement for a particular series, as well as a pari passu seller’s interest in each trust and (ii) in the case of SYNCT and SYNIT, any subordinated classes of notes that we own.
All of our securitized financings include early repayment triggers, referred to as early amortization events, including events related to material breaches of representations, warranties or covenants, inability or failure of the Bank to transfer loan receivables to the trusts as required under the securitization documents, failure to make required payments or deposits pursuant to the securitization documents, and certain insolvency-related events with respect to the related securitization depositor, Synchrony (solely with respect to SYNCT) or the Bank. In addition, an early amortization event will occur with respect to a series if the excess spread as it relates to a particular series or for the trust, as applicable, falls below zero. Following an early amortization event, principal collections on the loan receivables in the applicable trust are applied to repay principal of the trust's asset-backed securities rather than being available on a revolving basis to fund the origination activities of our business. The occurrence of an early amortization event also would limit or terminate our ability to issue future series out of the trust in which the early amortization event occurred. No early amortization event has occurred with respect to any of the securitized financings in SYNCT, SFT or SYNIT.
The following table summarizes for each of our trusts the three-month rolling average excess spread at March 31, 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Note Principal Balance
($ in millions) | | # of Series
Outstanding | | Three-Month Rolling Average Excess Spread(1) |
| SYNCT | $ | 4,152 | | | 7 | | | ~18.0% to 20.4% |
| SFT | $ | 1,300 | | | 5 | | | 20.3 | % |
| SYNIT | $ | 850 | | | 1 | | | 15.2 | % |
______________________
(1)Represents the excess spread (generally calculated as interest income collected from the applicable pool of loan receivables less applicable net charge-offs, interest expense and servicing costs, divided by the aggregate principal amount of loan receivables in the applicable pool) for SFT or, in the case of SYNCT, a range of the excess spreads relating to the particular series issued within such trust or, in the case of SYNIT, the excess spread relating to the one outstanding series issued within such trust, in all cases omitting any series that have not been outstanding for at least three full monthly periods and calculated in accordance with the applicable trust or series documentation, for the three securitization monthly periods ended March 31, 2022.
Senior Unsecured Notes
The following table provides a summary of our outstanding fixed rate senior unsecured notes at March 31, 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issuance Date | | Interest Rate(1) | | Maturity | | Principal Amount Outstanding(2) |
| ($ in millions) | | | | | | |
| Fixed rate senior unsecured notes: | | | | | | |
| Synchrony Financial | | | | | | |
| August 2014 | | 4.250% | | August 2024 | | 1,250 | |
| July 2015 | | 4.500% | | July 2025 | | 1,000 | |
| August 2016 | | 3.700% | | August 2026 | | 500 | |
| December 2017 | | 3.950% | | December 2027 | | 1,000 | |
| March 2019 | | 4.375% | | March 2024 | | 600 | |
| March 2019 | | 5.150% | | March 2029 | | 650 | |
| July 2019 | | 2.850% | | July 2022 | | 750 | |
| October 2021 | | 2.875% | | October 2031 | | 750 | |
| Synchrony Bank | | | | | | |
| June 2017 | | 3.000% | | June 2022 | | 750 | |
| Total fixed rate senior unsecured notes | | | | | | $ | 7,250 | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
______________________
(1)Weighted average interest rate of all senior unsecured notes at March 31, 2022 was 3.88%.
(2)The amounts shown exclude unamortized debt discounts, premiums and issuance costs.
Short-Term Borrowings
Except as described above, there were no material short-term borrowings for the periods presented.
Other
At March 31, 2022, we had more than $25.0 billion of unencumbered assets in the Bank available to be used to generate additional liquidity through secured borrowings or asset sales or to be pledged to the Federal Reserve Board for credit at the discount window.
Covenants
The indenture pursuant to which our senior unsecured notes have been issued includes various covenants. If we do not satisfy any of these covenants, the maturity of amounts outstanding thereunder may be accelerated and become payable. We were in compliance with all of these covenants at March 31, 2022.
At March 31, 2022, we were not in default under any of our credit facilities.
Credit Ratings
Our borrowing costs and capacity in certain funding markets, including securitizations and senior and subordinated debt, may be affected by the credit ratings of the Company, the Bank and the ratings of our asset-backed securities.
The table below reflects our current credit ratings and outlooks:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| S&P | | Fitch Ratings |
| Synchrony Financial | | | |
| Senior unsecured debt | BBB- | | BBB- |
| Preferred stock | BB- | | B+ |
| Outlook for Synchrony Financial senior unsecured debt | Stable | | Stable |
| Synchrony Bank | | | |
| Senior unsecured debt | BBB | | BBB- |
| Outlook for Synchrony Bank senior unsecured debt | Stable | | Stable |
In addition, certain of the asset-backed securities issued by SYNCT and SYNIT are rated by Fitch, S&P and/or Moody’s. A credit rating is not a recommendation to buy, sell or hold securities, may be subject to revision or withdrawal at any time by the assigning rating organization, and each rating should be evaluated independently of any other rating. Downgrades in these credit ratings could materially increase the cost of our funding from, and restrict our access to, the capital markets.
Liquidity
____________________________________________________________________________________________
We seek to ensure that we have adequate liquidity to sustain business operations, fund asset growth, satisfy debt obligations and to meet regulatory expectations under normal and stress conditions.
We maintain policies outlining the overall framework and general principles for managing liquidity risk across our business, which is the responsibility of our Asset and Liability Management Committee, a subcommittee of the Risk Committee of our Board of Directors. We employ a variety of metrics to monitor and manage liquidity. We perform regular liquidity stress testing and contingency planning as part of our liquidity management process. We evaluate a range of stress scenarios including Company specific and systemic events that could impact funding sources and our ability to meet liquidity needs.
We maintain a liquidity portfolio, which at March 31, 2022 had $14.7 billion of liquid assets, primarily consisting of cash and equivalents and short-term obligations of the U.S. Treasury, less cash in transit which is not considered to be liquid, compared to $13.0 billion of liquid assets at December 31, 2021. The increase in liquid assets was primarily due to the excess cash flows from operations and the seasonality of our business. We believe our liquidity position at March 31, 2022 remains strong as we continue to operate in a period of uncertain economic conditions and we will continue to closely monitor our liquidity as economic conditions change.
As additional sources of liquidity, at March 31, 2022, we had an aggregate of $2.6 billion of undrawn committed capacity on our securitized financings, subject to customary borrowing conditions, from private lenders under our securitization programs and $0.5 billion of undrawn committed capacity under our unsecured revolving credit facility with private lenders, and we had more than $25.0 billion of unencumbered assets in the Bank available to be used to generate additional liquidity through secured borrowings or asset sales or to be pledged to the Federal Reserve Board for credit at the discount window.
As a general matter, investments included in our liquidity portfolio are expected to be highly liquid, giving us the ability to readily convert them to cash. The level and composition of our liquidity portfolio may fluctuate based upon the level of expected maturities of our funding sources as well as operational requirements and market conditions.
We rely significantly on dividends and other distributions and payments from the Bank for liquidity; however, bank regulations, contractual restrictions and other factors limit the amount of dividends and other distributions and payments that the Bank may pay to us. For a discussion of regulatory restrictions on the Bank’s ability to pay dividends, see “Regulation—Risk Factors Relating to Regulation—We are subject to restrictions that limit our ability to pay dividends and repurchase our common stock; the Bank is subject to restrictions that limit its ability to pay dividends to us, which could limit our ability to pay dividends, repurchase our common stock or make payments on our indebtedness” and “Regulation—Regulation Relating to Our Business—Savings Association Regulation—Dividends and Stock Repurchases” in our 2021 Form 10-K.
Capital
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Our primary sources of capital have been earnings generated by our business and existing equity capital. We seek to manage capital to a level and composition sufficient to support the risks of our business, meet regulatory requirements, adhere to rating agency targets and support future business growth. The level, composition and utilization of capital are influenced by changes in the economic environment, strategic initiatives and legislative and regulatory developments. Within these constraints, we are focused on deploying capital in a manner that will provide attractive returns to our stockholders.
Synchrony is not currently required to conduct stress tests. See “Regulation—Regulation Relating to Our Business—Recent Legislative and Regulatory Developments” in our 2021 Form 10-K. In addition, while we have not been subject to the Federal Reserve Board's formal capital plan submission requirements to-date, we submitted a capital plan to the Federal Reserve Board in 2022. While not required, our capital plan process does include certain internal stress testing.
Dividend and Share Repurchases
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common Stock Cash Dividends Declared | | Month of Payment | | Amount per Common Share | | Amount |
| ($ in millions, except per share data) | | | | | | |
Three months ended March 31, 2022 | | February 2022 | | $ | 0.22 | | | $ | 114 | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Total dividends declared | | | | $ | 0.22 | | | $ | 114 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Preferred Stock Cash Dividends Declared | | Month of Payment | | Amount per Preferred Share | | Amount |
| ($ in millions, except per share data) | | | | | | |
Three months ended March 31, 2022 | | February 2022 | | $ | 14.06 | | | $ | 10 | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Total dividends declared | | | | $ | 14.06 | | | $ | 10 | |
In April 2022, we announced that our Board approved plans to increase our quarterly common stock dividend by 5% to $0.23 per common share commencing in the third quarter of 2022. The declaration and payment of future dividends to holders of our common and preferred stock will be at the discretion of the Board and will depend on many factors. For a discussion of regulatory and other restrictions on our ability to pay dividends and repurchase stock, see “Regulation—Risk Factors Relating to Regulation—We are subject to restrictions that limit our ability to pay dividends and repurchase our common stock; the Bank is subject to restrictions that limit its ability to pay dividends to us, which could limit our ability to pay dividends, repurchase our common stock or make payments on our indebtedness” in our 2021 Form 10-K.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common Shares Repurchased Under Publicly Announced Programs | | Total Number of Shares
Purchased | | Dollar Value of Shares
Purchased |
| ($ and shares in millions) | | | | |
Three months ended March 31, 2022 | | 22.0 | | | $ | 967 | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Total | | 22.0 | | | $ | 967 | |
During the first quarter of 2022, we repurchased $967 million of common stock as part of the share repurchase programs announced in 2021, with remaining authorized share repurchase capacity of $251 million under the 2021 program.
In addition, in April 2022, we announced that our Board approved an incremental share repurchase authorization of $2.8 billion through June 2023, resulting in total share repurchase authorization of $3.1 billion. In all instances, the share repurchase programs are subject to market conditions and other factors, including legal and regulatory restrictions and required approvals.
Regulatory Capital Requirements - Synchrony Financial
As a savings and loan holding company, we are required to maintain minimum capital ratios, under the applicable U.S. Basel III capital rules. For more information, see “Regulation—Savings and Loan Holding Company Regulation” in our 2021 Form 10-K.
For Synchrony Financial to be a well-capitalized savings and loan holding company, Synchrony Bank must be well-capitalized and Synchrony Financial must not be subject to any written agreement, order, capital directive, or prompt corrective action directive issued by the Federal Reserve Board to meet and maintain a specific capital level for any capital measure. At March 31, 2022, Synchrony Financial met all the requirements to be deemed well-capitalized.
The following table sets forth the composition of our capital ratios for the Company calculated under the Basel III Standardized Approach rules at March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basel III |
| | At March 31, 2022 | | At December 31, 2021 |
| ($ in millions) | Amount | | Ratio(1) | | Amount | | Ratio(1) |
| Total risk-based capital | $ | 14,360 | | | 17.2 | % | | $ | 15,122 | | | 17.8 | % |
| Tier 1 risk-based capital | $ | 13,254 | | | 15.9 | % | | $ | 14,003 | | | 16.5 | % |
| Tier 1 leverage | $ | 13,254 | | | 13.9 | % | | $ | 14,003 | | | 14.7 | % |
| Common equity Tier 1 capital | $ | 12,520 | | | 15.0 | % | | $ | 13,269 | | | 15.6 | % |
| Risk-weighted assets | $ | 83,251 | | | | | $ | 84,950 | | | |
______________________
(1)Tier 1 leverage ratio represents total Tier 1 capital as a percentage of total average assets, after certain adjustments. All other ratios presented above represent the applicable capital measure as a percentage of risk-weighted assets.
The Company elected to adopt the option provided by the interim final rule issued by joint federal bank regulatory agencies, which largely delayed the effects of CECL on our regulatory capital through December 31, 2021. Beginning in the first quarter of 2022, the effects are now being phased-in over a three-year transitional period through 2024, collectively the “CECL regulatory capital transition adjustment”. The effects of CECL on our regulatory capital will be fully phased-in beginning in the first quarter of 2025. For more information, see “Capital—Regulatory Capital Requirements - Synchrony Financial” in our 2021 Form 10-K.
Capital amounts and ratios in the above table all reflect the applicable CECL regulatory capital transition adjustment for each period. The decrease in our common equity Tier 1 capital ratio compared to December 31, 2021 was primarily due to the first year phase-in of the impact of CECL on our regulatory capital, which reduced our CET1 ratio by approximately 60 basis points.
Regulatory Capital Requirements - Synchrony Bank
At March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, the Bank met all applicable requirements to be deemed well-capitalized pursuant to OCC regulations and for purposes of the Federal Deposit Insurance Act. The following table sets forth the composition of the Bank’s capital ratios calculated under the Basel III Standardized Approach rules at March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, and also reflects the applicable CECL regulatory capital transition adjustment for each period.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | At March 31, 2022 | | At December 31, 2021 | | Minimum to be Well-Capitalized under Prompt Corrective Action Provisions |
| ($ in millions) | Amount | | Ratio | | Amount | | Ratio | | Ratio |
| Total risk-based capital | $ | 13,703 | | | 18.0 | % | | $ | 14,091 | | | 18.3 | % | | 10.0% |
| Tier 1 risk-based capital | $ | 12,692 | | | 16.7 | % | | $ | 13,075 | | | 16.9 | % | | 8.0% |
| Tier 1 leverage | $ | 12,692 | | | 14.6 | % | | $ | 13,075 | | | 15.1 | % | | 5.0% |
| Common equity Tier 1 capital | $ | 12,692 | | | 16.7 | % | | $ | 13,075 | | | 16.9 | % | | 6.5% |
Failure to meet minimum capital requirements can result in the initiation of certain mandatory and possibly additional discretionary actions by regulators that, if undertaken, could limit our business activities and have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. See “Regulation—Risk Factors Relating to Regulation—Failure by Synchrony and the Bank to meet applicable capital adequacy and liquidity requirements could have a material adverse effect on us” in our 2021 Form 10-K.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements and Unfunded Lending Commitments
____________________________________________________________________________________________
We do not have any material off-balance sheet arrangements, including guarantees of third-party obligations. Guarantees are contracts or indemnification agreements that contingently require us to make a guaranteed payment or perform an obligation to a third-party based on certain trigger events. At March 31, 2022, we had not recorded any contingent liabilities in our Condensed Consolidated Statement of Financial Position related to any guarantees. See Note 5 - Variable Interest Entities to our condensed consolidated financial statements for more information on our investment commitments for unconsolidated variable interest entity (“VIE's”).
We extend credit, primarily arising from agreements with customers for unused lines of credit on our credit cards, in the ordinary course of business. Each unused credit card line is unconditionally cancellable by us. See Note 4 - Loan Receivables and Allowance for Credit Losses to our condensed consolidated financial statements for more information on our unfunded lending commitments.
Critical Accounting Estimates
____________________________________________________________________________________________
In preparing our condensed consolidated financial statements, we have identified certain accounting estimates and assumptions that we consider to be the most critical to an understanding of our financial statements because they involve significant judgments and uncertainties. The critical accounting estimates we have identified relate to allowance for credit losses and fair value measurements. These estimates reflect our best judgment about current, and for some estimates future, economic and market conditions and their effects based on information available as of the date of these financial statements. If these conditions change from those expected, it is reasonably possible that these judgments and estimates could change, which may result in incremental losses on loan receivables, or material changes to our Condensed Consolidated Statement of Financial Position, among other effects. See “Management's Discussion and Analysis—Critical Accounting Estimates” in our 2021 Form 10-K, for a detailed discussion of these critical accounting estimates.
Regulation and Supervision
____________________________________________________________________________________________
Our business, including our relationships with our customers, is subject to regulation, supervision and examination under U.S. federal, state and foreign laws and regulations. These laws and regulations cover all aspects of our business, including lending and collection practices, treatment of our customers, safeguarding deposits, customer privacy and information security, capital structure, liquidity, dividends and other capital distributions, transactions with affiliates, and conduct and qualifications of personnel. Such laws and regulations directly and indirectly affect key drivers of our profitability, including, for example, capital and liquidity, product offerings, risk management, and costs of compliance.
As a savings and loan holding company and a financial holding company, Synchrony is subject to regulation, supervision and examination by the Federal Reserve Board. As a large provider of consumer financial services, we are also subject to regulation, supervision and examination by the CFPB.
The Bank is a federally chartered savings association. As such, the Bank is subject to regulation, supervision and examination by the OCC, which is its primary regulator, and by the CFPB. In addition, the Bank, as an insured depository institution, is supervised by the FDIC.
See “Regulation” in our 2021 Form 10-K for additional information on regulations that are currently applicable to us. See also “—Capital” above, for discussion of the impact of regulations and supervision on our capital and liquidity, including our ability to pay dividends and repurchase stock.
ITEM 1. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Synchrony Financial and subsidiaries
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Earnings (Unaudited)
____________________________________________________________________________________________
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions, except per share data) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Interest income: | | | | | | | |
| Interest and fees on loans (Note 4) | $ | 4,008 | | | $ | 3,732 | | | | | |
| Interest on cash and debt securities | 14 | | | 10 | | | | | |
| Total interest income | 4,022 | | | 3,742 | | | | | |
| Interest expense: | | | | | | | |
| Interest on deposits | 127 | | | 170 | | | | | |
| Interest on borrowings of consolidated securitization entities | 33 | | | 51 | | | | | |
| Interest on senior unsecured notes | 73 | | | 82 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total interest expense | 233 | | | 303 | | | | | |
| Net interest income | 3,789 | | | 3,439 | | | | | |
| Retailer share arrangements | (1,104) | | | (989) | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Provision for credit losses (Note 4) | 521 | | | 334 | | | | | |
| Net interest income, after retailer share arrangements and provision for credit losses | 2,164 | | | 2,116 | | | | | |
| Other income: | | | | | | | |
| Interchange revenue | 230 | | | 171 | | | | | |
| Debt cancellation fees | 89 | | | 69 | | | | | |
| Loyalty programs | (258) | | | (179) | | | | | |
| Other | 47 | | | 70 | | | | | |
| Total other income | 108 | | | 131 | | | | | |
| Other expense: | | | | | | | |
| Employee costs | 402 | | | 364 | | | | | |
| Professional fees | 210 | | | 190 | | | | | |
| Marketing and business development | 116 | | | 95 | | | | | |
| Information processing | 145 | | | 131 | | | | | |
| Other | 166 | | | 152 | | | | | |
| Total other expense | 1,039 | | | 932 | | | | | |
| Earnings before provision for income taxes | 1,233 | | | 1,315 | | | | | |
| Provision for income taxes (Note 12) | 301 | | | 290 | | | | | |
| Net earnings | $ | 932 | | | $ | 1,025 | | | | | |
| Net earnings available to common stockholders | $ | 922 | | | $ | 1,014 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Earnings per share | | | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | 1.79 | | | $ | 1.74 | | | | | |
| Diluted | $ | 1.77 | | | $ | 1.73 | | | | | |
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
Synchrony Financial and subsidiaries
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Unaudited)
____________________________________________________________________________________________
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Net earnings | $ | 932 | | | $ | 1,025 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | | | | | |
| Debt securities | (50) | | | (6) | | | | | |
| Currency translation adjustments | (2) | | | 2 | | | | | |
| Employee benefit plans | — | | | (1) | | | | | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | (52) | | | (5) | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Comprehensive income | $ | 880 | | | $ | 1,020 | | | | | |
Amounts presented net of taxes.
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
Synchrony Financial and subsidiaries
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Financial Position (Unaudited)
____________________________________________________________________________________________
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | At March 31, 2022 | | At December 31, 2021 |
| Assets | | | |
| Cash and equivalents | $ | 10,541 | | | $ | 8,337 | |
| Debt securities (Note 3) | 4,677 | | | 5,283 | |
| Loan receivables: (Notes 4 and 5) | | | |
| Unsecuritized loans held for investment | 59,643 | | | 60,211 | |
| Restricted loans of consolidated securitization entities | 19,273 | | | 20,529 | |
| Total loan receivables | 78,916 | | | 80,740 | |
| Less: Allowance for credit losses | (8,651) | | | (8,688) | |
| Loan receivables, net | 70,265 | | | 72,052 | |
| Loan receivables held for sale (Note 4) | 4,046 | | | 4,361 | |
| Goodwill | 1,105 | | | 1,105 | |
| Intangible assets, net (Note 6) | 1,149 | | | 1,168 | |
| Other assets | 3,484 | | | 3,442 | |
| Total assets | $ | 95,267 | | | $ | 95,748 | |
| | | |
| Liabilities and Equity | | | |
| Deposits: (Note 7) | | | |
| Interest-bearing deposit accounts | $ | 63,180 | | | $ | 61,911 | |
| Non-interest-bearing deposit accounts | 395 | | | 359 | |
| Total deposits | 63,575 | | | 62,270 | |
| Borrowings: (Notes 5 and 8) | | | |
| Borrowings of consolidated securitization entities | 6,139 | | | 7,288 | |
| | | |
| Senior unsecured notes | 7,221 | | | 7,219 | |
| Total borrowings | 13,360 | | | 14,507 | |
| Accrued expenses and other liabilities | 4,914 | | | 5,316 | |
| Total liabilities | $ | 81,849 | | | $ | 82,093 | |
| | | |
| Equity: | | | |
Preferred stock, par share value $0.001 per share; 750,000 shares authorized; 750,000 shares issued and outstanding at both March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021 and aggregate liquidation preference of $750 at both March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021 | $ | 734 | | | $ | 734 | |
Common Stock, par share value $0.001 per share; 4,000,000,000 shares authorized; 833,984,684 shares issued at both March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021; 506,223,095 and 526,830,205 shares outstanding at March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively | 1 | | | 1 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | 9,643 | | | 9,669 | |
| Retained earnings | 15,003 | | | 14,245 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss): | | | |
| Debt securities | (46) | | | 4 | |
| Currency translation adjustments | (28) | | | (26) | |
| Employee benefit plans | (47) | | | (47) | |
Treasury stock, at cost; 327,761,589 and 307,154,479 shares at March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively | (11,842) | | | (10,925) | |
| | | |
| Total equity | 13,418 | | | 13,655 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 95,267 | | | $ | 95,748 | |
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
Synchrony Financial and subsidiaries
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity (Unaudited)
____________________________________________________________________________________________
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Preferred Stock | | Common Stock | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
($ in millions,
shares in thousands) | Shares Issued | | Amount | | Shares Issued | | Amount | | Additional Paid-in Capital | | | | Retained Earnings | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | | Treasury Stock | | Total Equity | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at January 1, 2021 | 750 | | | $ | 734 | | | 833,985 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 9,570 | | | | | $ | 10,621 | | | $ | (51) | | | $ | (8,174) | | | $ | 12,701 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net earnings | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | 1,025 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,025 | | | |
| Other comprehensive income | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | — | | | (5) | | | — | | | (5) | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchases of treasury stock | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | — | | | — | | | (200) | | | (200) | | | |
| Stock-based compensation | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 22 | | | | | (37) | | | — | | | 72 | | | 57 | | | |
Dividends - preferred stock ($14.06 per share) | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | (11) | | | — | | | — | | | (11) | | | |
Dividends - common stock ($0.22 per share) | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | (128) | | | — | | | — | | | (128) | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at March 31, 2021 | 750 | | | $ | 734 | | | 833,985 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 9,592 | | | | | $ | 11,470 | | | $ | (56) | | | $ | (8,302) | | | $ | 13,439 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Preferred Stock | | Common Stock | | | | | | | | | | | | |
($ in millions,
shares in thousands) | Shares Issued | | Amount | | Shares Issued | | Amount | | Additional Paid-in Capital | | | | Retained Earnings | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | | Treasury Stock | | Total Equity |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at January 1, 2022 | 750 | | | $ | 734 | | | 833,985 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 9,669 | | | | | $ | 14,245 | | | $ | (69) | | | $ | (10,925) | | | $ | 13,655 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net earnings | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | 932 | | | — | | | — | | | 932 | |
| Other comprehensive income | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | — | | | (52) | | | — | | | (52) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchases of treasury stock | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | — | | | — | | | (968) | | | (968) | |
| Stock-based compensation | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (26) | | | | | (50) | | | — | | | 51 | | | (25) | |
Dividends - preferred stock ($14.06 per share) | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | (10) | | | — | | | — | | | (10) | |
Dividends - common stock ($0.22 per share) | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | (114) | | | — | | | — | | | (114) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at March 31, 2022 | 750 | | | $ | 734 | | | 833,985 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 9,643 | | | | | $ | 15,003 | | | $ | (121) | | | $ | (11,842) | | | $ | 13,418 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
Synchrony Financial and subsidiaries
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows (Unaudited)
____________________________________________________________________________________________
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, |
($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Cash flows - operating activities | | | |
| Net earnings | $ | 932 | | | $ | 1,025 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to cash provided from operating activities | | | |
| Provision for credit losses | 521 | | | 334 | |
| Deferred income taxes | 49 | | | 114 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 107 | | | 95 | |
| (Increase) decrease in interest and fees receivable | 65 | | | 288 | |
| (Increase) decrease in other assets | (12) | | | 87 | |
| Increase (decrease) in accrued expenses and other liabilities | (413) | | | (234) | |
| All other operating activities | 147 | | | 130 | |
| Cash provided from (used for) operating activities | 1,396 | | | 1,839 | |
| | | |
| Cash flows - investing activities | | | |
| Maturity and sales of debt securities | 1,998 | | | 2,514 | |
| Purchases of debt securities | (1,478) | | | (1,621) | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Net (increase) decrease in loan receivables, including held for sale | 1,415 | | | 3,996 | |
| All other investing activities | (117) | | | (252) | |
| Cash provided from (used for) investing activities | 1,818 | | | 4,637 | |
| | | |
| Cash flows - financing activities | | | |
| Borrowings of consolidated securitization entities | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of securitized debt | — | | | 250 | |
| Maturities and repayment of securitized debt | (1,150) | | | (868) | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Dividends paid on preferred stock | (10) | | | (11) | |
| Net increase (decrease) in deposits | 1,302 | | | (35) | |
| Purchases of treasury stock | (968) | | | (200) | |
| Dividends paid on common stock | (114) | | | (128) | |
| All other financing activities | (36) | | | 13 | |
| Cash provided from (used for) financing activities | (976) | | | (979) | |
| | | |
| Increase (decrease) in cash and equivalents, including restricted amounts | 2,238 | | | 5,497 | |
| Cash and equivalents, including restricted amounts, at beginning of period | 8,686 | | | 11,604 | |
| Cash and equivalents at end of period: | | | |
| Cash and equivalents | 10,541 | | | 16,620 | |
| Restricted cash and equivalents included in other assets | 383 | | | 481 | |
| Total cash and equivalents, including restricted amounts, at end of period | $ | 10,924 | | | $ | 17,101 | |
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
Synchrony Financial and subsidiaries
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)
____________________________________________________________________________________________
NOTE 1. BUSINESS DESCRIPTION
Synchrony Financial (the “Company”) provides a range of credit products through financing programs it has established with a diverse group of national and regional retailers, local merchants, manufacturers, buying groups, industry associations and healthcare service providers. We primarily offer private label, Dual Card, co-brand and general purpose credit cards, as well as short- and long-term installment loans, and savings products insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”) through Synchrony Bank (the “Bank”).
References to the “Company”, “we”, “us” and “our” are to Synchrony Financial and its consolidated subsidiaries unless the context otherwise requires.
NOTE 2. BASIS OF PRESENTATION AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements were prepared in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”).
Preparing financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires us to make estimates based on assumptions about current, and for some estimates, future, economic and market conditions (for example, unemployment, housing, interest rates and market liquidity) which affect reported amounts and related disclosures in our condensed consolidated financial statements. Although our current estimates contemplate current conditions and how we expect them to change in the future, as appropriate, it is reasonably possible that actual conditions could be different than anticipated in those estimates, which could materially affect our results of operations and financial position. Among other effects, such changes could result in incremental losses on loan receivables, future impairments of debt securities, goodwill and intangible assets, increases in reserves for contingencies, establishment of valuation allowances on deferred tax assets and increases in our tax liabilities.
We primarily conduct our business within the United States and Canada and substantially all of our revenues are from U.S. customers. The operating activities conducted by our non-U.S. affiliates use the local currency as their functional currency. The effects of translating the financial statements of these non-U.S. affiliates to U.S. dollars are included in equity. Asset and liability accounts are translated at period-end exchange rates, while revenues and expenses are translated at average rates for the respective periods.
Consolidated Basis of Presentation
The Company’s financial statements have been prepared on a consolidated basis. Under this basis of presentation, our financial statements consolidate all of our subsidiaries – i.e., entities in which we have a controlling financial interest, most often because we hold a majority voting interest.
To determine if we hold a controlling financial interest in an entity, we first evaluate if we are required to apply the variable interest entity (“VIE”) model to the entity, otherwise the entity is evaluated under the voting interest model. Where we hold current or potential rights that give us the power to direct the activities of a VIE that most significantly impact the VIE’s economic performance (“power”) combined with a variable interest that gives us the right to receive potentially significant benefits or the obligation to absorb potentially significant losses (“significant economics”), we have a controlling financial interest in that VIE. Rights held by others to remove the party with power over the VIE are not considered unless one party can exercise those rights unilaterally. We consolidate certain securitization entities under the VIE model because we have both power and significant economics. See Note 5. Variable Interest Entities.
Interim Period Presentation
The condensed consolidated financial statements and notes thereto are unaudited. These statements include all adjustments (consisting of normal recurring accruals) that we considered necessary to present a fair statement of our results of operations, financial position and cash flows. The results reported in these condensed consolidated financial statements should not be considered as necessarily indicative of results that may be expected for the entire year. These condensed consolidated financial statements should be read in conjunction with our 2021 annual consolidated financial statements and the related notes in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021 (our "2021 Form 10-K").
New Accounting Standards
Recently Issued But Not Yet Adopted Accounting Standards
In March 2022, the FASB issued ASU No. 2022-02, Financial Instruments – Credit Losses (Topic 326): Troubled Debt Restructurings and Vintage Disclosures. This ASU eliminates the separate recognition and measurement guidance for Troubled Debt Restructurings ("TDRs") by creditors. The elimination of the TDR guidance may be adopted prospectively for loan modifications after adoption or on a modified retrospective basis, which would also apply to loans previously modified, resulting in a cumulative effect adjustment to retained earnings in the period of adoption for changes in the allowance for credit losses. This guidance is effective for the Company on January 1, 2023, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impacts of the guidance.
See Note 2. Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies to our 2021 annual consolidated financial statements in our 2021 Form 10-K, for additional information on our other significant accounting policies.
NOTE 3. DEBT SECURITIES
All of our debt securities are classified as available-for-sale and are held to meet our liquidity objectives or to comply with the Community Reinvestment Act (“CRA”). Our debt securities consist of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| March 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 |
| | | Gross | | Gross | | | | | | Gross | | Gross | | |
| Amortized | | unrealized | | unrealized | | Estimated | | Amortized | | unrealized | | unrealized | | Estimated |
| ($ in millions) | cost | | gains | | losses | | fair value | | cost | | gains | | losses | | fair value |
| U.S. government and federal agency | $ | 2,362 | | | $ | — | | | $ | (26) | | | $ | 2,336 | | | $ | 2,222 | | | $ | — | | | $ | (2) | | | $ | 2,220 | |
| State and municipal | 11 | | | — | | | — | | | 11 | | | 13 | | | — | | | — | | | 13 | |
Residential mortgage-backed(a) | 555 | | | 1 | | | (17) | | | 539 | | | 597 | | | 12 | | | (3) | | | 606 | |
Asset-backed(b) | 1,801 | | | — | | | (18) | | | 1,783 | | | 2,432 | | | 2 | | | (4) | | | 2,430 | |
| Other | 8 | | | — | | | — | | | 8 | | | 13 | | | 1 | | | — | | | 14 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | $ | 4,737 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | (61) | | | $ | 4,677 | | | $ | 5,277 | | | $ | 15 | | | $ | (9) | | | $ | 5,283 | |
_______________________
(a) All of our residential mortgage-backed securities have been issued by government-sponsored entities and are collateralized by U.S. mortgages. At March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, $129 million and $145 million of residential mortgage-backed securities, respectively, are pledged by the Bank as collateral to the Federal Reserve to secure Federal Reserve Discount Window advances.
(b) Our asset-backed securities are collateralized by credit card and auto loans.
The following table presents the estimated fair values and gross unrealized losses of our available-for-sale debt securities:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| In loss position for |
| Less than 12 months | | 12 months or more |
| | | Gross | | | | Gross |
| Estimated | | unrealized | | Estimated | | unrealized |
| ($ in millions) | fair value | | losses | | fair value | | losses |
| At March 31, 2022 | | | | | | | |
| U.S. government and federal agency | $ | 1,786 | | | $ | (24) | | | $ | 50 | | | $ | (2) | |
| State and municipal | 10 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Residential mortgage-backed | 361 | | | (9) | | | 102 | | | (8) | |
| Asset-backed | 1,535 | | | (18) | | | 14 | | | — | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | $ | 3,692 | | | $ | (51) | | | $ | 166 | | | $ | (10) | |
| | | | | | | |
| At December 31, 2021 | | | | | | | |
| U.S. government and federal agency | $ | 563 | | | $ | (2) | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| State and municipal | 4 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Residential mortgage-backed | 105 | | | (2) | | | 27 | | | (1) | |
| Asset-backed | 1,653 | | | (4) | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | $ | 2,325 | | | $ | (8) | | | $ | 27 | | | $ | (1) | |
We regularly review debt securities for impairment resulting from credit loss using both qualitative and quantitative criteria, as necessary based on the composition of the portfolio at period end. Based on our assessment, no material impairments for credit losses were recognized during the period.
We presently do not intend to sell our debt securities that are in an unrealized loss position and believe that it is not more likely than not that we will be required to sell these securities before recovery of our amortized cost.
Contractual Maturities of Investments in Available-for-Sale Debt Securities
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amortized | | Estimated | | Weighted |
| At March 31, 2022 ($ in millions) | cost | | fair value | | Average yield (a) |
| Due | | | | | |
| Within one year | $ | 2,617 | | | $ | 2,610 | | | 0.5 | % |
| After one year through five years | $ | 1,565 | | | $ | 1,528 | | | 0.8 | % |
| After five years through ten years | $ | 302 | | | $ | 298 | | | 1.9 | % |
| After ten years | $ | 253 | | | $ | 241 | | | 1.7 | % |
| | | | | |
_____________________(a)Weighted average yield is calculated based on the amortized cost of each security. In calculating yield, no adjustment has been made with respect to any tax-exempt obligations.
We expect actual maturities to differ from contractual maturities because borrowers have the right to prepay certain obligations.
There were no material realized gains or losses recognized for the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021.
Although we generally do not have the intent to sell any specific securities held at March 31, 2022, in the ordinary course of managing our debt securities portfolio, we may sell securities prior to their maturities for a variety of reasons, including diversification, credit quality, yield, liquidity requirements and funding obligations.
NOTE 4. LOAN RECEIVABLES AND ALLOWANCE FOR CREDIT LOSSES
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | March 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 |
| Credit cards | $ | 74,596 | | | $ | 76,628 | |
| Consumer installment loans | 2,719 | | | 2,675 | |
| Commercial credit products | 1,530 | | | 1,372 | |
| Other | 71 | | | 65 | |
Total loan receivables, before allowance for credit losses(a)(b) | $ | 78,916 | | | $ | 80,740 | |
_______________________
(a)Total loan receivables include $19.3 billion and $20.5 billion of restricted loans of consolidated securitization entities at March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively. See Note 5. Variable Interest Entities for further information on these restricted loans.
(b)At March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, loan receivables included deferred costs, net of deferred income, of $213 million and $211 million, respectively.
Loan Receivables Held for Sale
At March 31, 2022, $4.0 billion of loan receivables associated with our program agreements with Gap Inc. and BP are classified as loan receivables held for sale on our Condensed Consolidated Statement of Financial Position. Restricted loans of our consolidated securitization entities at March 31, 2022 include $978 million of the loan receivables held for sale. See Note 5. Variable Interest Entities for further information. The sale of both portfolios, which are subject to customary closing conditions, are expected to be completed in the second quarter of 2022.
Allowance for Credit Losses
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | | | | | Balance at January 1, 2022 | | Provision charged to operations | | Gross charge-offs | | Recoveries | | Other | | | | Balance at
March 31, 2022 |
| Credit cards | | | | | $ | 8,512 | | | $ | 482 | | | $ | (719) | | | $ | 189 | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | 8,464 | |
| Consumer installment loans | | | | | 115 | | | 17 | | | (21) | | | 4 | | | — | | | | | 115 | |
| Commercial credit products | | | | | 59 | | | 22 | | | (12) | | | 1 | | | — | | | | | 70 | |
| Other | | | | | 2 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | | 2 | |
| Total | | | | | $ | 8,688 | | | $ | 521 | | | $ | (752) | | | $ | 194 | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | 8,651 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | Balance at January 1, 2021 | | Provision charged to operations | | Gross charge-offs | | Recoveries | | Other | | Balance at
March 31, 2021 |
| Credit cards | $ | 10,076 | | | $ | 341 | | | $ | (901) | | | $ | 219 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 9,735 | |
| Consumer installment loans | 127 | | | (18) | | | (15) | | | 5 | | | 1 | | | 100 | |
| Commercial credit products | 61 | | | 10 | | | (9) | | | 2 | | | — | | | 64 | |
| Other | 1 | | | 1 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 2 | |
| Total | $ | 10,265 | | | $ | 334 | | | $ | (925) | | | $ | 226 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 9,901 | |
Our allowance for credit losses at March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021 reflects our estimate of expected credit losses for the life of the loan receivables on our consolidated statement of financial position.
The reasonable and supportable forecast period used in our estimate of credit losses at March 31, 2022 was 12 months, consistent with the forecast period utilized since the adoption of CECL. Beyond the reasonable and supportable forecast period, we revert to historical loss information at the loan receivables segment level over a 6-month period, gradually increasing the weight of historical losses by an equal amount each month during the reversion period, and utilize historical loss information thereafter for the remaining life of the portfolio. The reversion period and methodology remain unchanged since the adoption of CECL.
Losses on loan receivables are estimated and recognized upon origination of the loan, based on expected credit losses for the life of the loan balance at March 31, 2022. Expected credit loss estimates are developed using both quantitative models and qualitative adjustments, and incorporates a macroeconomic forecast, as described within the 2021 Form 10-K. The current and forecasted economic conditions at the balance sheet date influenced our current estimate of expected credit losses. These conditions are relatively consistent as compared to December 31, 2021, reflecting recent trends in customer payment behavior, partially offset by an uncertain macroeconomic environment. Our allowance for credit losses remained relatively flat at $8.7 billion during the three months ended March 31, 2022 primarily due to these conditions. See Note 2. Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies to our 2021 annual consolidated financial statements in our 2021 Form 10-K, for additional information on our significant accounting policies related to our allowance for credit losses.
Delinquent and Non-accrual Loans
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At March 31, 2022 ($ in millions) | 30-89 days delinquent | | 90 or more days delinquent | | Total past due | | 90 or more days delinquent and accruing | | Total non-accruing |
| Credit cards | $ | 1,103 | | | $ | 1,000 | | | $ | 2,103 | | | $ | 1,000 | | | $ | — | |
| Consumer installment loans | 30 | | | 6 | | | 36 | | | — | | | 6 | |
| Commercial credit products | 35 | | | 20 | | | 55 | | | 20 | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total delinquent loans | $ | 1,168 | | | $ | 1,026 | | | $ | 2,194 | | | $ | 1,020 | | | $ | 6 | |
| Percentage of total loan receivables | 1.5 | % | | 1.3 | % | | 2.8 | % | | 1.3 | % | | — | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At December 31, 2021 ($ in millions) | 30-89 days delinquent | | 90 or more days delinquent | | Total past due | | 90 or more days delinquent and accruing | | Total non-accruing |
| Credit cards | $ | 1,111 | | | $ | 923 | | | $ | 2,034 | | | $ | 923 | | | $ | — | |
| Consumer installment loans | 35 | | | 6 | | | 41 | | | — | | | 6 | |
| Commercial credit products | 26 | | | 13 | | | 39 | | | 13 | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total delinquent loans | $ | 1,172 | | | $ | 942 | | | $ | 2,114 | | | $ | 936 | | | $ | 6 | |
| Percentage of total loan receivables | 1.5 | % | | 1.2 | % | | 2.6 | % | | 1.2 | % | | — | % |
Delinquency trends are the primary credit quality indicator for our consumer installment loans, which we use to monitor credit quality and risk within the portfolio. Total consumer installment past due of $36 million and $41 million at March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively, were not material.
Troubled Debt Restructurings
We use certain loan modification programs for borrowers experiencing financial difficulties. These loan modification programs include interest rate reductions and payment deferrals in excess of three months, which were not part of the terms of the original contract. Our TDR loans do not include loans that are classified as loan receivables held for sale.
We have both internal and external loan modification programs. We use long-term modification programs for borrowers experiencing financial difficulty as a loss mitigation strategy to improve long-term collectability of the loans that are classified as TDRs. The long-term program involves changing the structure of the loan to a fixed payment loan with a maturity no longer than 60 months and reducing the interest rate on the loan. The long-term program does not normally provide for the forgiveness of unpaid principal but may allow for the reversal of certain unpaid interest or fee assessments. We also make loan modifications for customers who request financial assistance through external sources, such as consumer credit counseling agency programs. These loans typically receive a reduced interest rate but continue to be subject to the original minimum payment terms and do not normally include waiver of unpaid principal, interest or fees. The following table provides information on our TDR loan modifications during the periods presented:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Credit cards | $ | 223 | | | $ | 261 | | | | | |
| Consumer installment loans | — | | | — | | | | | |
| Commercial credit products | 1 | | | 1 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | $ | 224 | | | $ | 262 | | | | | |
Our allowance for credit losses on TDRs is generally measured based on the difference between the recorded loan receivable and the present value of the expected future cash flows, discounted at the original effective interest rate of the loan. Interest income from loans accounted for as TDRs is accounted for in the same manner as other accruing loans.
The following table provides information about loans classified as TDRs and specific reserves. We do not evaluate credit card loans on an individual basis but instead estimate an allowance for credit losses on a collective basis.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At March 31, 2022 ($ in millions) | Total recorded
investment | | Related allowance | | Net recorded investment | | Unpaid principal balance |
| Credit cards | $ | 1,193 | | | $ | (496) | | | $ | 697 | | | $ | 1,071 | |
| Consumer installment loans | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Commercial credit products | 3 | | | (1) | | | 2 | | | 3 | |
| Total | $ | 1,196 | | | $ | (497) | | | $ | 699 | | | $ | 1,074 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At December 31, 2021 ($ in millions) | Total recorded
investment | | Related allowance | | Net recorded investment | | Unpaid principal balance |
| Credit cards | $ | 1,171 | | | $ | (481) | | | $ | 690 | | | $ | 1,053 | |
| Consumer installment loans | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Commercial credit products | 3 | | | (1) | | | 2 | | | 3 | |
| Total | $ | 1,174 | | | $ | (482) | | | $ | 692 | | | $ | 1,056 | |
Financial Effects of TDRs
As part of our loan modifications for borrowers experiencing financial difficulty, we may provide multiple concessions to minimize our economic loss and improve long-term loan performance and collectability. The following table presents the types and financial effects of loans modified and accounted for as TDRs during the periods presented:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | 2022 | | 2021 |
| ($ in millions) | Interest income recognized during period when loans were modified | | Interest income that would have been recorded with original terms | | Average recorded investment | | Interest income recognized during period when loans were modified | | Interest income that would have been recorded with original terms | | Average recorded investment |
| Credit cards | $ | 9 | | | $ | 77 | | | $ | 1,183 | | | $ | 11 | | | $ | 79 | | | $ | 1,273 | |
| Consumer installment loans | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Commercial credit products | — | | | — | | | 3 | | | — | | | — | | | 4 | |
| Total | $ | 9 | | | $ | 77 | | | $ | 1,186 | | | $ | 11 | | | $ | 79 | | | $ | 1,277 | |
Payment Defaults
The following table presents the type, number and amount of loans accounted for as TDRs that enrolled in a modification plan within the previous 12 months from the applicable balance sheet date and experienced a payment default and charged-off during the periods presented.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | 2022 | | 2021 |
| ($ in millions) | Accounts defaulted | | Loans defaulted | | Accounts defaulted | | Loans defaulted |
| Credit cards | 18,072 | | | $ | 42 | | | 16,933 | | | $ | 47 | |
| Consumer installment loans | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Commercial credit products | 38 | | | — | | | 38 | | — | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | 18,110 | | | $ | 42 | | | 16,971 | | | $ | 47 | |
Credit Quality Indicators
Our loan receivables portfolio includes both secured and unsecured loans. Secured loan receivables are largely comprised of consumer installment loans secured by equipment. Unsecured loan receivables are largely comprised of our open-ended consumer and commercial revolving credit card loans. As part of our credit risk management activities, on an ongoing basis, we assess overall credit quality by reviewing information related to the performance of a customer’s account with us, including delinquency information, as well as information from credit bureaus relating to the customer’s broader credit performance. We utilize VantageScore credit scores to assist in our assessment of credit quality. VantageScore credit scores are obtained at origination of the account and are refreshed, at a minimum quarterly, but could be as often as weekly, to assist in predicting customer behavior. We categorize these credit scores into the following three credit score categories: (i) 651 or higher, which are considered the strongest credits; (ii) 591 to 650, considered moderate credit risk; and (iii) 590 or less, which are considered weaker credits. There are certain customer accounts for which a VantageScore score is not available where we use alternative sources to assess their credit and predict behavior. The following table provides the most recent VantageScore scores available for our customers at March 31, 2022, December 31, 2021 and March 31, 2021, respectively, as a percentage of each class of loan receivable. The table below excludes 0.4%, 0.4% and 0.6% of our total loan receivables balance at each of March 31, 2022, December 31, 2021 and March 31, 2021, respectively, which represents those customer accounts for which a VantageScore score is not available.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| March 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 | | March 31, 2021 |
| 651 or | | 591 to | | 590 or | | 651 or | | 591 to | | 590 or | | 651 or | | 591 to | | 590 or |
| higher | | 650 | | | less | | higher | | 650 | | | less | | higher | | 650 | | | less |
| Credit cards | 76 | % | | 18 | % | | 6 | % | | 78 | % | | 17 | % | | 5 | % | | 77 | % | | 18 | % | | 5 | % |
| Consumer installment loans | 79 | % | | 17 | % | | 4 | % | | 79 | % | | 17 | % | | 4 | % | | 79 | % | | 17 | % | | 4 | % |
| Commercial credit products | 92 | % | | 5 | % | | 3 | % | | 92 | % | | 5 | % | | 3 | % | | 93 | % | | 4 | % | | 3 | % |
Unfunded Lending Commitments
We manage the potential risk in credit commitments by limiting the total amount of credit, both by individual customer and in total, by monitoring the size and maturity of our portfolios and by applying the same credit standards for all of our credit products. Unused credit card lines available to our customers totaled approximately $437 billion and $431 billion at March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively. While these amounts represented the total available unused credit card lines, we have not experienced and do not anticipate that all of our customers will access their entire available line at any given point in time.
Interest Income by Product
The following table provides additional information about our interest and fees on loans, including merchant discounts, from our loan receivables, including held for sale:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
Credit cards(a) | $ | 3,913 | | | $ | 3,657 | | | | | |
| Consumer installment loans | 66 | | | 53 | | | | | |
| Commercial credit products | 28 | | | 21 | | | | | |
| Other | 1 | | | 1 | | | | | |
| Total | $ | 4,008 | | | $ | 3,732 | | | | | |
_______________________(a)Interest income on credit cards that was reversed related to accrued interest receivables written off was $247 million and $305 million for the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
NOTE 5. VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES
We use VIEs to securitize loan receivables and arrange asset-backed financing in the ordinary course of business. Investors in these entities only have recourse to the assets owned by the entity and not to our general credit. We do not have implicit support arrangements with any VIE and we did not provide non-contractual support for previously transferred loan receivables to any of these VIEs in the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021. Our VIEs are able to accept new loan receivables and arrange new asset-backed financings, consistent with the requirements and limitations on such activities placed on the VIE by existing investors. Once an account has been designated to a VIE, the contractual arrangements we have require all existing and future loan receivables originated under such account to be transferred to the VIE. The amount of loan receivables held by our VIEs in excess of the minimum amount required under the asset-backed financing arrangements with investors may be removed by us under removal of accounts provisions. All loan receivables held by a VIE are subject to claims of third-party investors.
In evaluating whether we have the power to direct the activities of a VIE that most significantly impact its economic performance, we consider the purpose for which the VIE was created, the importance of each of the activities in which it is engaged and our decision-making role, if any, in those activities that significantly determine the entity’s economic performance as compared to other economic interest holders. This evaluation requires consideration of all facts and circumstances relevant to decision-making that affects the entity’s future performance and the exercise of professional judgment in deciding which decision-making rights are most important.
In determining whether we have the right to receive benefits or the obligation to absorb losses that could potentially be significant to a VIE, we evaluate all of our economic interests in the entity, regardless of form (debt, equity, management and servicing fees, and other contractual arrangements). This evaluation considers all relevant factors of the entity’s design, including: the entity’s capital structure, contractual rights to earnings or losses, subordination of our interests relative to those of other investors, as well as any other contractual arrangements that might exist that could have the potential to be economically significant. The evaluation of each of these factors in reaching a conclusion about the potential significance of our economic interests is a matter that requires the exercise of professional judgment.
We consolidate VIEs where we have the power to direct the activities that significantly affect the VIEs' economic performance, typically because of our role as either servicer or administrator for the VIEs. The power to direct exists because of our role in the design and conduct of the servicing of the VIEs’ assets as well as directing certain affairs of the VIEs, including determining whether and on what terms debt of the VIEs will be issued.
The loan receivables in these entities have risks and characteristics similar to our other financing receivables and were underwritten to the same standard. Accordingly, the performance of these assets has been similar to our other comparable loan receivables, and the blended performance of the pools of receivables in these entities reflects the eligibility criteria that we apply to determine which receivables are selected for transfer. Contractually, the cash flows from these financing receivables must first be used to pay third-party debt holders, as well as other expenses of the entity. Excess cash flows, if any, are available to us. The creditors of these entities have no claim on our other assets.
The table below summarizes the assets and liabilities of our consolidated securitization VIEs described above:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | March 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 |
| Assets | | | |
Loan receivables, net(a) | $ | 17,408 | | | $ | 18,594 | |
| Loan receivables held for sale | 978 | | | 1,398 | |
Other assets(b) | 322 | | | 292 | |
| Total | $ | 18,708 | | | $ | 20,284 | |
| | | | |
| Liabilities | | | |
| Borrowings | $ | 6,139 | | | $ | 7,288 | |
| Other liabilities | 12 | | | 14 | |
| Total | $ | 6,151 | | | $ | 7,302 | |
_______________________
(a) Includes $1.9 billion and $1.9 billion of related allowance for credit losses resulting in gross restricted loans of $19.3 billion and $20.5 billion at March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively.
(b) Includes $319 million and $288 million of segregated funds held by the VIEs at March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively, which are classified as restricted cash and equivalents and included as a component of other assets in our Condensed Consolidated Statements of Financial Position.
The balances presented above are net of intercompany balances and transactions that are eliminated in our condensed consolidated financial statements.
We provide servicing for all of our consolidated VIEs. Collections are required to be placed into segregated accounts owned by each VIE in amounts that meet contractually specified minimum levels. These segregated funds are invested in cash and cash equivalents and are restricted as to their use, principally to pay maturing principal and interest on debt and the related servicing fees. Collections above these minimum levels are remitted to us on a daily basis.
Income (principally, interest and fees on loans) earned by our consolidated VIEs was $939 million and $1.1 billion for the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Related expenses consisted primarily of provision for credit losses of $46 million and $(57) million for the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively, and interest expense of $33 million and $51 million for the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively. These amounts do not include intercompany transactions, principally fees and interest, which are eliminated in our condensed consolidated financial statements.
Non-consolidated VIEs
As part of our community reinvestment initiatives, we invest in affordable housing properties and receive affordable housing tax credits for these investments. These investments included in our Condensed Consolidated Statement of Financial Position totaled $430 million and $441 million at March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively, and represents our total exposure for these entities. Additionally, we have other investments in non-consolidated VIEs which totaled $195 million and $184 million at March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively. At March 31, 2022, the Company also has investment commitments of $209 million related to these investments.
NOTE 6. INTANGIBLE ASSETS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | March 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 |
| ($ in millions) | | | Gross carrying amount | | Accumulated amortization | | Net | | Gross carrying amount | | Accumulated amortization | | Net |
| Customer-related | | | $ | 1,822 | | | $ | (1,257) | | | $ | 565 | | | $ | 1,797 | | | $ | (1,222) | | | $ | 575 | |
| Capitalized software and other | | | 1,456 | | | (872) | | | 584 | | | 1,407 | | | (814) | | | 593 | |
| Total | | | $ | 3,278 | | | $ | (2,129) | | | $ | 1,149 | | | $ | 3,204 | | | $ | (2,036) | | | $ | 1,168 | |
During the three months ended March 31, 2022, we recorded additions to intangible assets subject to amortization of $79 million, primarily related to capitalized software expenditures, as well as customer-related intangible assets.
Customer-related intangible assets primarily relate to retail partner contract acquisitions and extensions, as well as purchased credit card relationships. During the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021, we recorded additions to customer-related intangible assets subject to amortization of $26 million and $62 million, respectively, primarily related to payments made to acquire and extend certain retail partner relationships. These additions had a weighted average amortizable life of 5 years for both the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021.
Amortization expense related to retail partner contracts was $32 million for both the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021 and is included as a component of marketing and business development expense in our Condensed Consolidated Statements of Earnings. All other amortization expense was $61 million and $50 million for the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively, and is included as a component of other expense in our Condensed Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
NOTE 7. DEPOSITS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| March 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 |
| ($ in millions) | Amount | | Average rate(a) | | Amount | | Average rate(a) |
| Interest-bearing deposits | $ | 63,180 | | | 0.8 | % | | $ | 61,911 | | | 0.9 | % |
| Non-interest-bearing deposits | 395 | | | — | | | 359 | | | — | |
| Total deposits | $ | 63,575 | | | | | $ | 62,270 | | | |
____________________
(a)Based on interest expense for the three months ended March 31, 2022 and the year ended December 31, 2021 and average deposits balances.
At March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, interest-bearing deposits included $5.2 billion and $5.0 billion, respectively, of certificates of deposit that exceeded applicable FDIC insurance limits, which are generally $250,000 per depositor.
At March 31, 2022, our interest-bearing time deposits maturing for the remainder of 2022 and over the next four years and thereafter were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2023 | | 2024 | | 2025 | | 2026 | | Thereafter | |
| Deposits | $ | 12,357 | | | $ | 10,630 | | | $ | 3,157 | | | $ | 713 | | | $ | 671 | | | $ | 121 | | |
The above maturity table excludes $31.4 billion of demand deposits with no defined maturity, of which $28.8 billion are savings accounts. In addition, at March 31, 2022, we had $4.1 billion of broker network deposit sweeps procured through a program arranger who channels brokerage account deposits to us that are also excluded from the above maturity table. Unless extended, the contracts associated with these broker network deposit sweeps will terminate between 2023 and 2025.
NOTE 8. BORROWINGS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| March 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 |
| ($ in millions) | Maturity date | | Interest Rate | | Weighted average interest rate | | Outstanding Amount(a) | | Outstanding Amount(a) |
| Borrowings of consolidated securitization entities: | | | | | | | | | |
| Fixed securitized borrowings | 2022 - 2023 | | 2.34% - 3.87% | | 2.80 | % | | $ | 2,439 | | | $ | 3,188 | |
| Floating securitized borrowings | 2022 - 2024 | | 1.03% - 1.28% | | 1.12 | % | | 3,700 | | | 4,100 | |
| Total borrowings of consolidated securitization entities | | | | | 1.79 | % | | 6,139 | | | 7,288 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Senior unsecured notes: | | | | | | | | | |
| Synchrony Financial senior unsecured notes: | | | | | | | | | |
| Fixed senior unsecured notes | 2022 - 2031 | | 2.85% - 5.15% | | 3.98 | % | | 6,471 | | | 6,470 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Synchrony Bank senior unsecured notes: | | | | | | | | | |
| Fixed senior unsecured notes | 2022 | | 3.00% | | 3.00 | % | | 750 | | | 749 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total senior unsecured notes | | | | | 3.88 | % | | 7,221 | | | 7,219 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total borrowings | | | | | | | $ | 13,360 | | | $ | 14,507 | |
___________________(a)The amounts presented above for outstanding borrowings include unamortized debt premiums, discounts and issuance costs.
Debt Maturities
The following table summarizes the maturities of the principal amount of our borrowings of consolidated securitization entities and senior unsecured notes for the remainder of 2022 and over the next four years and thereafter:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2023 | | 2024 | | 2025 | | 2026 | | Thereafter | |
| Borrowings | $ | 3,858 | | | $ | 2,307 | | | $ | 3,325 | | | $ | 1,000 | | | $ | 500 | | | $ | 2,400 | | |
Credit Facilities
As additional sources of liquidity, we have undrawn committed capacity under certain credit facilities, primarily related to our securitization programs.
At March 31, 2022, we had an aggregate of $2.6 billion of undrawn committed capacity under our securitization financings, subject to customary borrowing conditions, from private lenders under our securitization programs, and an aggregate of $0.5 billion of undrawn committed capacity under our unsecured revolving credit facility with private lenders.
NOTE 9. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
For a description of how we estimate fair value, see Note 2. Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies in our 2021 annual consolidated financial statements in our 2021 Form 10-K.
The following tables present our assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis.
Recurring Fair Value Measurements | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At March 31, 2022 ($ in millions) | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total(a) |
| Assets | | | | | | | |
| Debt securities | | | | | | | |
| U.S. government and federal agency | $ | — | | | $ | 2,336 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 2,336 | |
| State and municipal | — | | | — | | | 11 | | | 11 | |
| Residential mortgage-backed | — | | | 539 | | | — | | | 539 | |
| Asset-backed | — | | | 1,783 | | | — | | | 1,783 | |
| Other | — | | | — | | | 8 | | | 8 | |
Other(b) | 15 | | | — | | | 34 | | | 49 | |
| Total | $ | 15 | | | $ | 4,658 | | | $ | 53 | | | $ | 4,726 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | |
Other(c) | — | | | — | | | 10 | | | 10 | |
| Total | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 10 | |
| | | | | | | |
| At December 31, 2021 ($ in millions) | | | | | | | |
| Assets | | | | | | | |
| Debt securities | | | | | | | |
| U.S. government and federal agency | $ | — | | | $ | 2,220 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 2,220 | |
| State and municipal | — | | | — | | | 13 | | | 13 | |
| Residential mortgage-backed | — | | | 606 | | | — | | | 606 | |
| Asset-backed | — | | | 2,430 | | | — | | | 2,430 | |
| Other | — | | | — | | | 14 | | | 14 | |
Other(b) | 15 | | | — | | | 34 | | | 49 | |
| Total | $ | 15 | | | $ | 5,256 | | | $ | 61 | | | $ | 5,332 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | |
Other(c) | — | | | — | | | 14 | | | 14 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 14 | | | $ | 14 | |
_______________________
(a) For the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021, there were no fair value measurements transferred between levels.
(b) Other is primarily comprised of equity investments measured at fair value, which are included in Other assets in our Statement of Financial Position, as well as certain financial assets for which we have elected the fair value option which are included in Loan receivables in our Statement of Financial Position.
(c) Other is primarily comprised of certain financial liabilities for which we have elected the fair value option, which are included in Accrued expenses and other liabilities in our Statement of Financial Position.
Level 3 Fair Value Measurements
Our Level 3 recurring fair value measurements primarily relate to state and municipal and corporate debt instruments, which are valued using non-binding broker quotes or other third-party sources, and financial assets and liabilities for which we have elected the fair value option. See Note 2. Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies and Note 9. Fair Value Measurements in our 2021 annual consolidated financial statements in our 2021 Form 10-K for a description of our process to evaluate third-party pricing servicers. Our state and municipal debt securities are classified as available-for-sale with changes in fair value included in accumulated other comprehensive income.
The changes in our Level 3 assets and liabilities that are measured on a recurring basis for the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively, were not material.
Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities Carried at Other Than Fair Value
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Carrying | | Corresponding fair value amount |
| At March 31, 2022 ($ in millions) | value | | Total | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| Financial Assets | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial assets for which carrying values equal or approximate fair value: | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and equivalents(a) | $ | 10,541 | | | $ | 10,541 | | | $ | 10,541 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Other assets(a)(b) | $ | 383 | | | $ | 383 | | | $ | 383 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Financial assets carried at other than fair value: | | | | | | | | | |
Loan receivables, net(c) | $ | 70,246 | | | $ | 81,492 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 81,492 | |
Loan receivables held for sale(c) | $ | 4,046 | | | $ | 4,175 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 4,175 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Financial Liabilities | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial liabilities carried at other than fair value: | | | | | | | | | |
| Deposits | $ | 63,575 | | | $ | 63,615 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 63,615 | | | $ | — | |
| Borrowings of consolidated securitization entities | $ | 6,139 | | | $ | 6,155 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 2,451 | | | $ | 3,704 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Senior unsecured notes | $ | 7,221 | | | $ | 7,246 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 7,246 | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Carrying | | Corresponding fair value amount |
| At December 31, 2021 ($ in millions) | value | | Total | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| Financial Assets | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial assets for which carrying values equal or approximate fair value: | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and equivalents(a) | $ | 8,337 | | | $ | 8,337 | | | $ | 8,337 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Other assets(a)(b) | $ | 349 | | | $ | 349 | | | $ | 349 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Financial assets carried at other than fair value: | | | | | | | | | |
Loan receivables, net(c) | $ | 72,034 | | | $ | 84,483 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 84,483 | |
Loan receivables held for sale(c) | $ | 4,361 | | | $ | 4,499 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 4,499 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Financial Liabilities | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial liabilities carried at other than fair value: | | | | | | | | | |
| Deposits | $ | 62,270 | | | $ | 62,486 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 62,486 | | | $ | — | |
| Borrowings of consolidated securitization entities | $ | 7,288 | | | $ | 7,359 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 3,238 | | | $ | 4,121 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Senior unsecured notes | $ | 7,219 | | | $ | 7,662 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 7,662 | | | $ | — | |
_______________________
(a) For cash and equivalents and restricted cash and equivalents, carrying value approximates fair value due to the liquid nature and short maturity of these instruments.
(b) This balance relates to restricted cash and equivalents, which is included in other assets.
(c) Excludes financial assets for which we have elected the fair value option. Under certain retail partner program agreements, the expected sales proceeds in the event of a sale of their credit card portfolio may be limited to the amounts owed by our customers, which may be less than the fair value indicated above.
Equity Securities Without Readily Determinable Fair Values
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, |
| ($ in millions) | 2022 | | 2021 |
Carry Value(a) | $ | 242 | | | $ | 111 | |
Upward adjustments(b) | 7 | | | 32 | |
Downward adjustments(b) | (2) | | | — | |
_______________________(a) The carrying value as of December 31, 2021 was $232 million.
(b) Between January 1, 2018 and March 31, 2022, cumulative upward and downward carrying value adjustments were $188 million and $(10) million, respectively.
NOTE 10. REGULATORY AND CAPITAL ADEQUACY
As a savings and loan holding company and a financial holding company, we are subject to regulation, supervision and examination by the Federal Reserve Board and subject to the capital requirements as prescribed by Basel III capital rules and the requirements of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act. The Bank is a federally chartered savings association. As such, the Bank is subject to regulation, supervision and examination by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency of the U.S. Treasury (the “OCC”), which is its primary regulator, and by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (“CFPB”). In addition, the Bank, as an insured depository institution, is supervised by the FDIC.
Failure to meet minimum capital requirements can initiate certain mandatory and, possibly, additional discretionary actions by regulators that, if undertaken, could limit our business activities and have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial statements. Under capital adequacy guidelines, we must meet specific capital guidelines that involve quantitative measures of our assets, liabilities and certain off-balance-sheet items as calculated under regulatory accounting practices. The capital amounts and classifications are also subject to qualitative judgments by the regulators about components, risk weightings and other factors.
Quantitative measures established by regulation to ensure capital adequacy require us and the Bank to maintain minimum amounts and ratios (set forth in the tables below) of Total, Tier 1 and common equity Tier 1 capital (as defined in the regulations) to risk-weighted assets (as defined), and of Tier 1 capital to average assets (as defined).
For Synchrony Financial to be a well-capitalized savings and loan holding company, the Bank must be well-capitalized and Synchrony Financial must not be subject to any written agreement, order, capital directive, or prompt corrective action directive issued by the Federal Reserve Board to meet and maintain a specific capital level for any capital measure.
The Company elected to adopt the option provided by the interim final rule issued by joint federal bank regulatory agencies, which largely delayed the effects of CECL on its regulatory capital through December 31, 2021. Beginning in the first quarter of 2022, the effects are now being phased-in over a three-year period through 2024 and effects fully phased-in beginning in the first quarter of 2025. Under the interim final rule, the amount of adjustments to regulatory capital deferred until the phase-in period included both the initial impact of our adoption of CECL at January 1, 2020 and 25% of subsequent changes in our allowance for credit losses during the two-year period ended December 31, 2021, collectively the “CECL regulatory capital transition adjustment”. In 2022, only 75% of the CECL regulatory capital transition adjustment is now deferred in our regulatory capital amounts and ratios.
At March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, Synchrony Financial met all applicable requirements to be deemed well-capitalized pursuant to Federal Reserve Board regulations. At March 31, 2022 and December 31, 2021, the Bank also met all applicable requirements to be deemed well-capitalized pursuant to OCC regulations and for purposes of the Federal Deposit Insurance Act. There are no conditions or events subsequent to March 31, 2022 that management believes have changed the Company's or the Bank’s capital category.
The actual capital amounts, ratios and the applicable required minimums of the Company and the Bank are as follows:
Synchrony Financial
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At March 31, 2022 ($ in millions) | Actual | | Minimum for capital
adequacy purposes |
| Amount | | Ratio(a) | | Amount | | Ratio(b) |
| Total risk-based capital | $ | 14,360 | | | 17.2 | % | | $ | 6,660 | | | 8.0 | % |
| Tier 1 risk-based capital | $ | 13,254 | | | 15.9 | % | | $ | 4,995 | | | 6.0 | % |
| Tier 1 leverage | $ | 13,254 | | | 13.9 | % | | $ | 3,812 | | | 4.0 | % |
| Common equity Tier 1 Capital | $ | 12,520 | | | 15.0 | % | | $ | 3,746 | | | 4.5 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At December 31, 2021 ($ in millions) | Actual | | Minimum for capital
adequacy purposes |
| Amount | | Ratio(a) | | Amount | | Ratio(b) |
| Total risk-based capital | $ | 15,122 | | | 17.8 | % | | $ | 6,796 | | | 8.0 | % |
| Tier 1 risk-based capital | $ | 14,003 | | | 16.5 | % | | $ | 5,097 | | | 6.0 | % |
| Tier 1 leverage | $ | 14,003 | | | 14.7 | % | | $ | 3,800 | | | 4.0 | % |
| Common equity Tier 1 Capital | $ | 13,269 | | | 15.6 | % | | $ | 3,823 | | | 4.5 | % |
Synchrony Bank
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At March 31, 2022 ($ in millions) | Actual | | Minimum for capital
adequacy purposes | | Minimum to be well-capitalized under prompt corrective action provisions |
| Amount | | Ratio(a) | | Amount | | Ratio(b) | | Amount | | Ratio |
| Total risk-based capital | $ | 13,703 | | | 18.0 | % | | $ | 6,082 | | | 8.0 | % | | $ | 7,603 | | | 10.0 | % |
| Tier 1 risk-based capital | $ | 12,692 | | | 16.7 | % | | $ | 4,562 | | | 6.0 | % | | $ | 6,082 | | | 8.0 | % |
| Tier 1 leverage | $ | 12,692 | | | 14.6 | % | | $ | 3,484 | | | 4.0 | % | | $ | 4,356 | | | 5.0 | % |
| Common equity Tier I capital | $ | 12,692 | | | 16.7 | % | | $ | 3,421 | | | 4.5 | % | | $ | 4,942 | | | 6.5 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At December 31, 2021 ($ in millions) | Actual | | Minimum for capital
adequacy purposes | | Minimum to be well-capitalized under prompt corrective action provisions |
| Amount | | Ratio(a) | | Amount | | Ratio(b) | | Amount | | Ratio |
| Total risk-based capital | $ | 14,091 | | | 18.3 | % | | $ | 6,175 | | | 8.0 | % | | $ | 7,718 | | | 10.0 | % |
| Tier 1 risk-based capital | $ | 13,075 | | | 16.9 | % | | $ | 4,631 | | | 6.0 | % | | $ | 6,175 | | | 8.0 | % |
| Tier 1 leverage | $ | 13,075 | | | 15.1 | % | | $ | 3,455 | | | 4.0 | % | | $ | 4,318 | | | 5.0 | % |
| Common equity Tier I capital | $ | 13,075 | | | 16.9 | % | | $ | 3,473 | | | 4.5 | % | | $ | 5,017 | | | 6.5 | % |
_______________________
(a)Capital ratios are calculated based on the Basel III Standardized Approach rules. Capital amounts and ratios at March 31, 2022 and at December 31, 2021 in the above tables reflect the applicable CECL regulatory capital transition adjustment.
(b)At March 31, 2022 and at December 31, 2021, Synchrony Financial and the Bank also must maintain a capital conservation buffer of common equity Tier 1 capital in excess of minimum risk-based capital ratios by at least 2.5 percentage points to avoid limits on capital distributions and certain discretionary bonus payments to executive officers and similar employees.
The Bank may pay dividends on its stock, with consent or non-objection from the OCC and the Federal Reserve Board, among other things, if its regulatory capital would not thereby be reduced below the applicable regulatory capital requirements.
NOTE 11. EARNINGS PER SHARE
Basic earnings per share is computed by dividing earnings available to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings per common share reflects the assumed conversion of all dilutive securities.
The following table presents the calculation of basic and diluted earnings per common share:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended March 31, | | |
| (in millions, except per share data) | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Net earnings | $ | 932 | | | $ | 1,025 | | | | | |
| Preferred stock dividends | (10) | | | (11) | | | | | |
| Net earnings available to common stockholders | $ | 922 | | | $ | 1,014 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, basic | 515.3 | | | 583.3 | | | | | |
| Effect of dilutive securities | 4.2 | | | 4.2 | | | | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding, dilutive | 519.5 | | | 587.5 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Earnings per basic common share | $ | 1.79 | | | $ | 1.74 | | | | | |
| Earnings per diluted common share | $ | 1.77 | | | $ | 1.73 | | | | | |
We have issued certain stock-based awards under the Synchrony Financial 2014 Long-Term Incentive Plan. A total of 1 million shares for both the three months ended March 31, 2022 and 2021 related to these awards, were considered anti-dilutive and therefore were excluded from the computation of diluted earnings per common share.
NOTE 12. INCOME TAXES
Unrecognized Tax Benefits
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions) | March 31, 2022 | | December 31, 2021 |
Unrecognized tax benefits, excluding related interest expense and penalties(a) | $ | 244 | | | $ | 274 | |
Portion that, if recognized, would reduce tax expense and effective tax rate(b) | $ | 170 | | | $ | 160 | |
| | | |
| | | |
____________________(a)Interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits were not material for all periods presented.
(b)Comprised of federal unrecognized tax benefits and state and local unrecognized tax benefits net of the effects of associated U.S. federal income taxes. Excludes amounts attributable to any related valuation allowances resulting from associated increases in deferred tax assets.
We establish a liability that represents the difference between a tax position taken (or expected to be taken) on an income tax return and the amount of taxes recognized in our financial statements. The liability associated with the unrecognized tax benefits is adjusted periodically when new information becomes available. The amount of unrecognized tax benefits that is reasonably possible to be resolved in the next twelve months is expected to be $61 million, of which $25 million, if recognized, would reduce the Company's tax expense and effective tax rate.
In the current year, the Company executed a Memorandum of Understanding with the IRS to participate voluntarily in the IRS Compliance Assurance Process (“CAP”) program for the 2022 tax year, and thus the tax year is under IRS review. The IRS is also examining our 2021 tax year, and we expect the review will be substantially completed prior to filing the 2021 tax return in the current year. Additionally, we are under examination in various states going back to 2014.
We believe that there are no issues or claims that are likely to significantly impact our results of operations, financial position or cash flows. We further believe that we have made adequate provision for all income tax uncertainties that could result from such examinations.
NOTE 13. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS AND REGULATORY MATTERS
In the normal course of business, from time to time, we have been named as a defendant in various legal proceedings, including arbitrations, class actions and other litigation, arising in connection with our business activities. Certain of the legal actions include claims for substantial compensatory and/or punitive damages, or claims for indeterminate amounts of damages. We are also involved, from time to time, in reviews, investigations and proceedings (both formal and informal) by governmental agencies regarding our business (collectively, “regulatory matters”), which could subject us to significant fines, penalties, obligations to change our business practices or other requirements resulting in increased expenses, diminished income and damage to our reputation. We contest liability and/or the amount of damages as appropriate in each pending matter. In accordance with applicable accounting guidance, we establish an accrued liability for legal and regulatory matters when those matters present loss contingencies which are both probable and reasonably estimable.
Legal proceedings and regulatory matters are subject to many uncertain factors that generally cannot be predicted with assurance, and we may be exposed to losses in excess of any amounts accrued.
For some matters, we are able to determine that an estimated loss, while not probable, is reasonably possible. For other matters, including those that have not yet progressed through discovery and/or where important factual information and legal issues are unresolved, we are unable to make such an estimate. We currently estimate that the reasonably possible losses for legal proceedings and regulatory matters, whether in excess of a related accrued liability or where there is no accrued liability, and for which we are able to estimate a possible loss, are immaterial. This represents management’s estimate of possible loss with respect to these matters and is based on currently available information. This estimate of possible loss does not represent our maximum loss exposure. The legal proceedings and regulatory matters underlying the estimate will change from time to time and actual results may vary significantly from current estimates.
Our estimate of reasonably possible losses involves significant judgment, given the varying stages of the proceedings, the existence of numerous yet to be resolved issues, the breadth of the claims (often spanning multiple years), unspecified damages and/or the novelty of the legal issues presented. Based on our current knowledge, we do not believe that we are a party to any pending legal proceeding or regulatory matters that would have a material adverse effect on our condensed consolidated financial condition or liquidity. However, in light of the uncertainties involved in such matters, the ultimate outcome of a particular matter could be material to our operating results for a particular period depending on, among other factors, the size of the loss or liability imposed and the level of our earnings for that period, and could adversely affect our business and reputation.
Below is a description of certain of our regulatory matters and legal proceedings.
On November 2, 2018, a putative class action lawsuit, Retail Wholesale Department Store Union Local 338 Retirement Fund v. Synchrony Financial, et al., was filed in the U.S. District Court for the District of Connecticut, naming as defendants the Company and two of its officers. The lawsuit asserts violations of the Exchange Act for allegedly making materially misleading statements and/or omitting material information concerning the Company’s underwriting practices and private-label card business, and was filed on behalf of a putative class of persons who purchased or otherwise acquired the Company’s common stock between October 21, 2016 and November 1, 2018. The complaint seeks an award of unspecified compensatory damages, costs and expenses. On February 5, 2019, the court appointed Stichting Depositary APG Developed Markets Equity Pool as lead plaintiff for the putative class. On April 5, 2019, an amended complaint was filed, asserting a new claim for violations of the Securities Act in connection with statements in the offering materials for the Company’s December 1, 2017 note offering. The Securities Act claims are filed on behalf of persons who purchased or otherwise acquired Company bonds in or traceable to the December 1, 2017 note offering between December 1, 2017 and November 1, 2018. The amended complaint names as additional defendants two additional Company officers, the Company’s board of directors, and the underwriters of the December 1, 2017 note offering. The amended complaint is captioned Stichting Depositary APG Developed Markets Equity Pool and Stichting Depositary APG Fixed Income Credit Pool v. Synchrony Financial et al. On March 26, 2020, the District Court recaptioned the case In re Synchrony Financial Securities Litigation and on March 31, 2020, the District Court granted the defendants’ motion to dismiss the complaint with prejudice. On April 20, 2020, plaintiffs filed a notice to appeal the decision to the United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit. On February 16, 2021, the Court of Appeals affirmed the District Court’s dismissal of the Securities Act claims and all of the claims under the Exchange Act with the exception of a claim relating to a single statement on January 19, 2018 regarding whether Synchrony was receiving pushback on credit from its retail partners.
On January 28, 2019, a purported shareholder derivative action, Gilbert v. Keane, et al., was filed in the U.S. District Court for the District of Connecticut against the Company as a nominal defendant, and certain of the Company’s officers and directors. The lawsuit alleges breach of fiduciary duty claims based on the allegations raised by the plaintiff in the Stichting Depositar APG class action, unjust enrichment, waste of corporate assets, and that the defendants made materially misleading statements and/or omitted material information in violation of the Exchange Act. The complaint seeks a declaration that the defendants breached and/or aided and abetted the breach of their fiduciary duties to the Company, unspecified monetary damages with interest, restitution, a direction that the defendants take all necessary actions to reform and improve corporate governance and internal procedures, and attorneys’ and experts’ fees. On March 11, 2019, a second purported shareholder derivative action, Aldridge v. Keane, et al., was filed in the U.S. District Court for the District of Connecticut. The allegations in the Aldridge complaint are substantially similar to those in the Gilbert complaint. On March 26, 2020, the District Court recaptioned the Gilbert and Aldridge cases as In re Synchrony Financial Derivative Litigation.
On April 30, 2014 Belton et al. v. GE Capital Consumer Lending, a putative class action adversary proceeding was filed in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York. Plaintiff alleges that the Bank violates the discharge injunction under Section 524(a)(2) of the Bankruptcy Code by attempting to collect discharged debts and by failing to update and correct credit information to credit reporting agencies to show that such debts are no longer due and owing because they have been discharged in bankruptcy. Plaintiff seeks declaratory judgment, injunctive relief and an unspecified amount of damages. On December 15, 2014, the Bankruptcy Court entered an order staying the adversary proceeding pending an appeal to the District Court of the Bankruptcy Court’s order denying the Bank’s motion to compel arbitration. On October 14, 2015, the District Court reversed the Bankruptcy Court and on November 4, 2015, the Bankruptcy Court granted the Bank’s motion to compel arbitration. On March 4, 2019, on plaintiff’s motion for reconsideration, the District Court vacated its decision reversing the Bankruptcy Court and affirmed the Bankruptcy Court’s decision denying the Bank’s motion to compel arbitration. On June 16, 2020, the Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit denied the Bank’s appeal of the District Court’s decision. On October 5, 2021, the plaintiff filed a motion for preliminary approval of a class action settlement. Under the settlement, if approved by the court, the Bank will pay up to $8.5 million to class members, and implement or maintain certain practices with respect to credit reporting of sold accounts. On October 28, 2021, the Bankruptcy Court issued an order preliminarily approving the settlement. In February 2022, the District Court issued an order granting final approval of the settlement.
ITEM 3. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Market risk refers to the risk that a change in the level of one or more market prices, rates, indices, correlations or other market factors will result in losses for a position or portfolio. We are exposed to market risk primarily from changes in interest rates.
We borrow money from a variety of depositors and institutions in order to provide loans to our customers. Changes in market interest rates cause our net interest income to increase or decrease, as some of our assets and liabilities carry interest rates that fluctuate with market benchmarks. The interest rate benchmark for our floating rate assets is generally the prime rate, and the interest rate benchmark for our floating rate liabilities is generally either London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) or the federal funds rate. The prime rate and the LIBOR or federal funds rate could reset at different times or could diverge, leading to mismatches in the interest rates on our floating rate assets and floating rate liabilities. We are in the process of amending existing asset and liability contracts that reference LIBOR to reference a new benchmark rate.
The following table presents the approximate net interest income impacts forecasted over the next twelve months from an immediate and parallel change in interest rates affecting all interest rate sensitive assets and liabilities at March 31, 2022.
| | | | | | | | |
| Basis Point Change | | At March 31, 2022 |
| ($ in millions) | | |
| -100 basis points | | $ | (75) | |
| +100 basis points | | $ | (1) | |
For a more detailed discussion of our exposure to market risk and our transition from the LIBOR benchmark rate, refer to “Management's Discussion and Analysis—Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk” in our 2021 Form 10-K.
ITEM 4. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Under the direction of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act), and based on such evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of March 31, 2022.
No change in internal control over financial reporting occurred during the fiscal quarter ended March 31, 2022 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
PART II. OTHER INFORMATION
ITEM 1. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
For a description of legal proceedings, see Note 13. Legal Proceedings and Regulatory Matters to our condensed consolidated financial statements in Part 1, Item 1 of this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
There have been no material changes to the risk factors included in our 2021 Form 10-K under the heading “Risk Factors Relating to Our Business” and “Risk Factors Relating to Regulation”.
ITEM 2. UNREGISTERED SALES OF EQUITY SECURITIES AND USE OF PROCEEDS
The table below sets forth information regarding purchases of our common stock primarily related to our share repurchase program that were made by us or on our behalf during the three months ended March 31, 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| ($ in millions, except per share data) | Total Number of Shares Purchased(a) | | Average Price Paid Per Share(b) | | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Programs(c) | | Maximum Dollar Value of Shares That May Yet Be Purchased Under the Programs(b) |
January 1 - 31, 2022 | 5,661,679 | | | $ | 46.32 | | | 5,223,267 | | | $ | 976.0 | |
February 1 - 28, 2022 | 16,469,708 | | | 43.21 | | | 16,469,700 | | | 264.3 | |
March 1 - 31, 2022 | 775,649 | | | 39.75 | | | 333,744 | | | 250.9 | |
| Total | 22,907,036 | | | $ | 43.86 | | | 22,026,711 | | | $ | 250.9 | |
_______________________(a)Includes 438,412 shares, 8 shares and 441,905 shares withheld in January, February and March, respectively, to offset tax withholding obligations that occur upon the delivery of outstanding shares underlying performance stock awards, restricted stock awards or upon the exercise of stock options.
(b)Amounts exclude commission costs.
(c)In May 2021 the Board of Directors approved a share repurchase program of up to $2.9 billion. In December 2021, the Board of Directors authorized an increase to the May 2021 Share Repurchase Program of $1.0 billion through the period ending June 30, 2022. In addition, in April 2022, we announced that our Board approved an incremental share repurchase authorization of $2.8 billion through June 2023.
ITEM 3. DEFAULTS UPON SENIOR SECURITIES
None.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
ITEM 5. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
ITEM 6. EXHIBITS
EXHIBIT INDEX
| | | | | |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document - the instance document does not appear in the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
| 104 | The cover page from the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2022, formatted in Inline XBRL (included as Exhibit 101) |
______________________
*Filed electronically herewith.
†Portions of this exhibit have been redacted pursuant to Securities and Exchange Commission rules regarding confidential treatment. The locations where information has been redacted are indicated by the following notation "***".
Signatures
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
Synchrony Financial
(Registrant)
| | | | | | | | |
| April 21, 2022 | | /s/ Brian J. Wenzel Sr. |
| Date | | Brian J. Wenzel Sr.
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer
(Duly Authorized Officer and Principal Financial Officer) |